 |
 |
- Search
| J Audiol Otol > Volume 23(4); 2019 > Article |
|
Abstract
Diagnosis of pre-lingual hearing loss (HL) is difficult owing to the high number of genes responsible. The most frequent cause of HL is DFNB1 due to mutations in the GJB2 gene. It represents up to 40% of HL cases in some populations. In Iran, it has previously been shown that DFNB1 accounts for 16-18% of cases but varies among different ethnic groups. Here, we reviewed results from our three previous publications and data from other published mutation reports to provide a comprehensive collection of data for GJB2 mutations and HL in northern Iran. In total, 903 unrelated families from six different provinces, viz., Gilan, Mazandaran, Golestan, Ghazvin, Semnan, and Tehran, were included and analyzed for the type and prevalence of GJB2 mutations. A total of 23 different genetic variants were detected from which 18 GJB2 mutations were identified. GJB2 mutations were 20.7% in the studied northern provinces, which was significantly higher than that reported in southern populations of Iran. Moreover, a gradient in the frequency of GJB2 mutations from north to south Iran was observed. c.35delG was the most common mutation, accounting for 58.4% of the cases studied. This study suggests that c.35delG mutation in GJB2 is the most important cause of HL in northern Iran.
Hearing loss (HL) is a sensory impairment that affects millions of people worldwide, with the probability of approximately 1 in 1000 live births (http://hearing.screening.nhs.uk/nationalprog). Approximately, two-third of individuals with hearing impairment reside in developing countries, wherein more than 60% cases are attributed to genetic factors [1]. The genetic forms of HL are syndromic, which is accompanied by other specific abnormalities, and non-syndromic HL (NSHL), in which no additional abnormalities are observed. Autosomal recessive mode of inheritance (ARNSHL) comprises 80% of NSHL cases. ARNSHL is highly heterogeneous, with over 100 associated loci and >60 identified causative genes (http://hereditaryhearingloss.org/). GJB2 at the DFNB1 locus is responsible for 60% of all deafness cases, and over 100 GJB2 pathogenic variants have been reported with variable frequency among disparate world populations [2-11]. c.35delG accounts for >50% of GJB2-related NSHL in many western populations [12]. Other mutations are more origin specific. In the Japanese population, 235delC is more prevalent [3] and c.167delT is common in Ashkenazi Jews [2]. In individuals of Indian and Pakistani ancestry, c.71G>A is the common GJB2 variant [3]. Over the last decade, several studies have been conducted on the Iranian population to identify the mutation spectrum and prevalence of GJB2 mutations [13-23]. The different ethnicities coupled with the high frequency of familial marriages (38% on an average) [24] tend to change mutation frequencies among the ethnic groups [25]. Therefore, for accurate genetic counseling, studying certain ethnic groups is of high importance. In this study, we have summarized the published data on the frequency and profile of GJB2 mutations in 903 unrelated families from six different provinces, viz., Gilan, Mazandaran, Golestan, Ghazvin, Semnan, and Tehran, in north Iran compared to those in other parts of the country.
This study included results from our three previous publications on GJB2-related HL in Iran [19-36]. We also performed a PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar search using the search terms “GJB2 mutations”, “connexin 26”, and “Iran”. In the search results, we limited the search to humans with available information on molecular genetics of HL. Studies were included when the following three criteria were fulfilled: 1) inclusion of NSHL subjects, 2) known ethnicity of the tested subjects, and 3) detection of all GJB2 variants. Studies were excluded if HL was a result of environmental factors, such as infection, trauma, rubella, meningitis, mumps, ototoxic drugs, and premature birth. Research data, including data of 903 unrelated deaf families, from the north provinces were collected. The frequency and mutation type of 903 deaf families were extracted from relevant studies and categorized corresponding to the geographical boundaries. In silico analyses were also performed using the available software tools (Mutation Taster and SIFT; http://www.mutationtaster.org, https://sift.bii.a-star.edu.sg/) to predict the pathogenicity of the mutations.
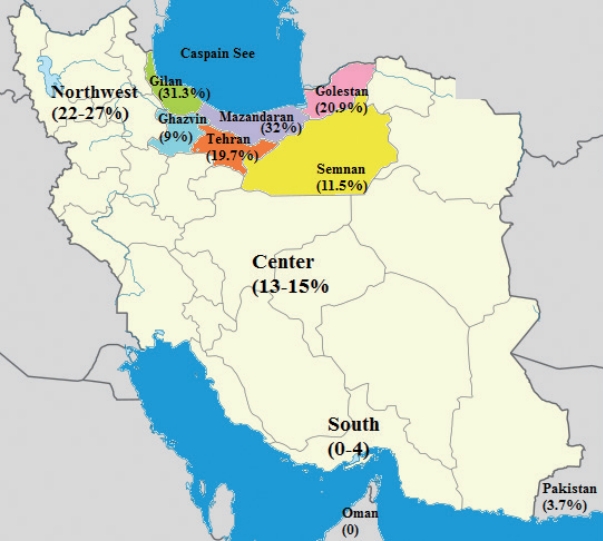
Data from 903 unrelated families from six provinces were analyzed (Table 1). The groups studied consisted of 429 families from Tehran (47.5%), 156 families from Gilan (17.3%), 111 families from Semnan (12.3%), 100 families from Mazandaran (11.1%), 85 families from Golestan (9.4%), and 22 families from Ghazvin (2.4%). Among these families, 66.5% reported parental consanguinity, whereas close consanguinity was denied in 33.5% cases (Table 2). GJB2 mutation allele frequencies of each studied group were 32%, 31.3%, 20.9%, 19.75%, 11.5%, and 9% in the total studied families (n=903) of Mazandaran, Gilan, Golestan, Tehran, Semnan, and Ghazvin, respectively (Fig. 1). When moving from the west to east and north to south of the studied provinces, a gradual decrease in GJB2 HL was observed.
In total, 30 different variants were identified, 22 of which were reported as pathogenic. These included c.-23+1G>A, c.35delG, c.71G>A, c.95G>A, c.136G>A, c.139G>T, c.167delT, c.224G>A, c.229T>C, c.230G>A, c.235delC, K102Q, c.313-326del, c.327-328delGG, c.358-360delGAG, c.326G>A, c.334-36delAA, c.427C>T, 463-464delTA, c.487A>G, c.511G>A, and c.551G>C. The allele variants identified in various Iranian ARSNSHL families are summarized in Table 3. In the studied populations, c.35delG was the most frequent mutation, accounting for 58.4% cases in the populations studied. The highest rate of c.35delG mutation was detected in the Gilan province with an allele frequency of 27.6%, whereas this rate was 6.3% in Semnan (Table 1). A specific combination of GJB2 mutation types and frequencies were observed in the different studied provinces (Table 3). A higher GJB2 mutation diversity (17 types) was identified in Tehran, whereas the lowest diversity was observed in Ghazvin (two types).
In this study, we reviewed the prevalence and type of GJB2 mutations in 903 deaf families from six provinces in northern Iran. GJB2 mutations accounted for 20.7% of HL cases. The genetic epidemiology of HL is very different in a country even in neighboring provinces because of subtle variations in their ethnic composition and founder effects [26]. The Iranian population is composed of many different ethnic groups; therefore, it is significant to discuss ethnicity-specific data. Accepting the northwest to southeast GJB2 HL gradient throughout Iran, our data showed a north to south gradient among Iranian populations with a GJB2 mutations frequency of 32% in Mazandaran and 9% in Ghazvin. A study performed by Chaleshtori, et al. [27] on 890 ARNSHL families showed that GJB2 mutations account for 14.6% HL cases in the Iranian population, and c.35delG mutation was the most frequent mutation (~75% of the reported GJB2 mutations).
Our results showed that the contribution of GJB2 mutations to ARNSHL was 32% in Mazandaran (north Iran), which is similar to the data from the Azer Turkish population in northwest Iran [28]. Bonyadi, et al. [28] screened 209 HL families from the Azerbijan and Ardebil provinces in northwest Iran for GJB2 mutations. They reported that GJB2 mutations were detected in 28% of the HL families studied and c.35delG was the most prevalent mutation, accounting for 64.5% of mutations, which is similar to the results reported for the Turkish population [29].
In the study performed by Bazazzadegan, et al. [30] on 111 deaf families, GJB2 mutations accounted for 11.5% HL cases in the Semnan province, which is approximately one-third of the frequency of GJB2 mutations in the Mazandaran province. In a previous study, we showed that GJB2 mutations explain the etiology of HL in 3.7% patients from the Hormozgan province in south of Iran [31]. On the basis of these results, it can be concluded that the incidence of GJB2 mutations decreases gradually in both west to east and north to south directions (Fig. 1), drawing the migration pathway of the initial founders.
Another finding of this study was the mutation rate of c.35delG in the Gilan province, which was different from that of Iranian population regions. Chaleshtori, et al. [27] screened 87 deaf families from the Gilan province in north Iran for DFNB1 mutations and reported that GJB2 mutations were found in 27.6% of the deaf families studied. Interestingly, c.35delG mutation was identified in 95.9% of GJB2 mutations in the Gilan province, whereas this mutation was absent in the Baluchi population (southeast Iran) [32]. According to our knowledge, this is the highest rate of c.35delG mutation reported from Iran so far. Results obtained for the carrier frequency of c.35delG mutation was 2.8% in the Gilan province, whereas it was 1% in the remaining Iranian groups [33]. However, this population is bounded in the north by the Caspian Sea and remains relatively isolated by mountains from other parts of Iran.
In our studied populations, the most frequent mutation was c.35delG, accounting for 58.4% of GJB2 mutations. c.35delG (deletion of guanine in position 30-35; rs80338939) is the most common mutation worldwide as well as in many countries in the Middle East, such as Turkey and north and northwest Iran [34]. The study of the geographical distribution of GJB2 mutations showed more allelic heterogeneity in the north compared to that in the south of Iran [31,35,36]. The four most frequent mutations of GJB2 in the north of Iran were c.35delG, c.71G>A, c.-23+1G>A, and c.551G>C and are responsible for ~66.3% of all pathogenic alleles in north Iran (Table 3). c.35delG mutation, which is rare among southern regions, accounts for 58.4% of GJB2 mutations in the northern populations. c.71G>A, c.-23+1G>A, and c.551G>C are the second, third, and fourth common mutations, with an occurrence of 2.9%, 2.45%, and 2.45%, respectively, of all pathogenic alleles.
p.Trp24*, a nonsense mutation, is because of c.71G>A transition, which changes TGG codon for tryptophan residue to a stop codon, leading to a truncated protein with probably no functional properties. c.71G>A is the most common mutation in Slovak Romany, Pakistan, and Indian populations [37-39]. The rate of carriers of c.71G>A mutation is 4.08% in the Pakistan population [8]. This mutation is observed at a high frequency in the Baluchi group (southeast Iran) and accounts for 80% of the mutant alleles in this ethnicity, whereas this rate was only 2.9% in our study population [40].
p.Arg184Pro, a missense variant, is the result of c.551G>C transition, which changes CGC codon for arginine residue to a CCC codon for proline, probably leading to a non-functional protein. This mutation has been reported in an Australian family for the first time [41]. In silico analyses are consistent with the pathogenicity of the mutation (Table 3). p.Arg184Pro is not the common mutation in Iranian populations, but this mutation is observed at a high frequency in north and northwest Iran because of founder effects [25].
The present data showed a particular combination of GJB2 mutation diversity in different provinces of north Iran. A higher GJB2 mutation diversity (17 types) was identified in the Tehran province, showing the co-existence of several different ethnic groups and marked immigration to the metropolitan during the last century. In contrast with high diversity in Tehran, we found a very low rate of diversity in some populations, such as Ghazvini who are probably isolated owing to cultural and geographical barriers.
The critical and specific position of Iran and the existence of various ethnic groups of different cultures suggest high heterogeneity throughout Iran, but specific intra-ethnic traditions, such as intragroup marriages, may result in high homogeneity in some loci and mutations within groups. GJB2 mutations are responsible for 20.7% cases of deaf families in the north, which is more than that in central Iran (13-15%), suggesting the migration pathway from the north to central Iran through the silk route. Regarding GJB2 mutations, c.35delG was the most common mutation first tested. In the studied populations, some mutations were frequent, which were detected in each group, e.g., the frequency of c.35delG mutation showed a high rate in the Gilan province (north Iran) accounting for 90.2% of the mutant alleles studied. In addition, the causes of HL in some populations, such as Golestani, are likely more homogenous than those in other parts of north Iran. The present study will help in improving genetic diagnosis, cascade screening, genetic counseling, and molecular epidemiology of HL in Irani populations, particularly of northern origin.
Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies
| Number | First author | Year | Province | Detection method | Case | Hearing loss type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chaleshtori | 2002 | Gilan | ARMS-PCR and sanger sequencing | 87 | ARNSHL | [35] |
| 2 | Bazazzadegan | 2012 | Gilan | Sanger sequencing | 69 | NSHL | [30] |
| 3 | Bazazzadegan | 2012 | Ghazvin | Sanger sequencing | 22 | NSHL | [30] |
| 4 | Hosseinipour | 2005 | Golestan | ARMS-PCR and sanger sequencing | 55 | ARNSHL | [19] |
| 5 | Bazazzadegan | 2012 | Golestan | Sanger sequencing | 30 | NSHL | [30] |
| 6 | Bazazzadegan | 2012 | Tehran | Sanger sequencing | 173 | NSHL | [30] |
| 7 | Chaleshtori | 2005 | Tehran | ARMS-PCR and sanger sequencing | 256 | ARNSHL | [36] |
| 8 | Chaleshtori | 2007 | Semnan | Sanger sequencing | 111 | NSHL | [27] |
| 9 | Bazazzadegan | 2012 | Mazandaran | Sanger sequencing | 100 | NSHL | [30] |
Table 2.
The frequency of consanguinity among different provinces of north Iran
| Province | Gilan | Mazandaran | Golestan | Tehran | Semnan | Ghazvin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consanguinity | 85 | 57 | 58 | 307 | 76 | 18 |
| Non-consanguinity | 71 | 43 | 27 | 122 | 35 | 4 |
| Total* | 156 | 100 | 85 | 429 | 111 | 22 |
Table 3.
GJB2 mutations, their frequencies and in silico analyses in six provinces of Iran
| Mutations | Gilan [30] | Gilan [35] | Mazandaran [30] | Golestan [30] | Golestan [19] | Ghazvin [30] | Tehran [36] | Tehran [30] | Semnan [27] | Mutation type | Classification |
Functional effect |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation taster | SIFT | ||||||||||||
| c.35delG | 39 (28.3) | 47 (27) | 47 (23.5) | 17 (28.3) | 10 (9.1) | 2 (4.5) | 48 (9.4) | 38 (10.1) | 14 (6.3) | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.71G>A | - | - | 2 (1) | - | - | - | 2 (0.4) | 4 (1.16) | 5 (2.25) | Missense | T | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.95G>A | - | - | 5 (2.5) | - | - | - | 2 (0.4) | 2 (0.58) | 1 (0.45) | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.136G>A | 2 (1.44) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.139G>T | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.2) | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.167delT | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.9) | - | 1 (0.2) | - | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.224G>A | - | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.29) | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.229T>C | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.230G>A | - | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | - | - | 2 (0.9) | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.235delC | 1 (0.72) | - | - | - | - | - | 6 (1.18) | - | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.257C>A | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.2) | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.313-326del | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 (0.58) | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.326G>A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.45) | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.327-328delGG | 1 (0.72) | 2 (1.15) | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.2) | - | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.334-336delAA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.29) | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.358-360delGAG | - | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | - | - | 7 (2.02) | - | Inframe deletion | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.427C>T | - | - | - | - | - | - | 3 (0.6) | 4 (1.16) | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.463-464delTA | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 (0.58) | - | Frameshift | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.487A>G | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 (0.4) | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | NA |
| c.511G>A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.551G>C | 1 (0.72) | - | 1 (0.5) | - | - | 2 (4.5) | 4 (0.8) | 3 (0.87) | - | Missense | NT | Disease causing | Damaging |
| c.-23+1G>A | 2 (1.44) | - | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1.6) | - | - | - | 4 (1.16) | 1 (0.45) | Splice site | T | Disease causing | NA |
| c.79G>A | 1 (0.72) | 2 (1.15) | - | - | 2 (1.8) | - | - | 2 (0.58) | 2 (0.9) | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Tolerated |
| c.186C>T | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.341A>G | - | 2 (1.15) | 1 (0.5) | - | 1 (0.9) | - | - | 1 (0.29) | 1 (0.45) | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.380G>A | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.457G>A | 3 (2.17) | 4 (2.3) | 5 (2.5) | 1 (1.6) | 2 (1.8) | - | 30 (5.9) | 4 (1.16) | 7 (3.15) | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.478G>A | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.29) | - | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.608T>C | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 (0.29) | - | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| c.-3558C>T | - | - | - | - | - | - | 21 (4.1) | - | - | Missense | NT | polymorphism | Benign |
| Normal | 88 | 117 | 133 | 41 | 94 | 40 | 389 | 269 | 187 | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 138 | 174 | 200 | 60 | 110 | 44 | 512 | 346 | 222 | - | - | - | - |
REFERENCES
1. Morton CC, Nance WE. Newborn hearing screening--a silent revolution. N Engl J Med 2006;354:2151–64.


2. Bakhchane A, Bousfiha A, Charoute H, Salime S, Detsouli M, Snoussi K, et al. Update of the spectrum of GJB2 gene mutations in 152 Moroccan families with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Eur J Med Genet 2016;59:325–9.


3. Nishio SY, Usami S. Deafness gene variations in a 1120 nonsyndromic hearing loss cohort: molecular epidemiology and deafness mutation spectrum of patients in Japan. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 2015;124 Suppl 1:49S–60S.


4. Hamelmann C, Amedofu GK, Albrecht K, Muntau B, Gelhaus A, Brobby GW, et al. Pattern of connexin 26 (GJB2) mutations causing sensorineural hearing impairment in Ghana. Hum Mut 2001;18:84–5.

5. Al-Qahtani MH, Baghlab I, Chaudhary AG, Abuzenadah AM, Bamanie A, Daghistani KJ, et al. Spectrum of GJB2 mutations in a cohort of nonsyndromic hearing loss cases from the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2010;14:79–83.


6. Azadegan-Dehkordi F, Ahmadi R, Koohiyan M, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M. Update of spectrum c.35delG and c.-23+1G>A mutations on the GJB2 gene in individuals with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Ann Hum Genet 2019;83:1–10.


7. Tlili A, Al Mutery A, Kamal Eddine Ahmad Mohamed W, Mahfood M, Hadj Kacem H. Prevalence of GJB2 mutations in affected individuals from United Arab Emirates with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2017;21:686–91.


8. Santos R, Wajid M, Pham TL, Hussan J, Ali G, Ahmad W, et al. Low prevalence of Connexin 26 (GJB2) variants in Pakistani families with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment. Clin Genet 2005;67:61–8.



9. Lee KY, Choi SY, Bae JW, Kim S, Chung KW, Drayna D, et al. Molecular analysis of the GJB2, GJB6 and SLC26A4 genes in Korean deafness patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2008;72:1301–9.



10. Dalamón V, Lotersztein V, Béhèran A, Lipovsek M, Diamante F, Pallares N, et al. GJB2 and GJB6 genes: molecular study and identification of novel GJB2 mutations in the hearing-impaired Argentinean population. Audiol Neurotol 2010;15:194–202.

11. Rădulescu L, Mârţu C, Birkenhäger R, Cozma S, Ungureanu L, Laszig R. Prevalence of mutations located at the dfnb1 locus in a population of cochlear implanted children in eastern Romania. Int J Pediatric Otorhinolaryngol 2012;76:90–4.

12. Green GE, Scott DA, McDonald JM, Woodworth GG, Sheffield VC, Smith RJ. Carrier rates in the midwestern United States for GJB2 mutations causing inherited deafness. JAMA 1999;281:2211–6.


13. Sadeghi A, Sanati MH, Alasti F, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M, Mahmoudian S, Ataei M. Contribution of GJB2 mutations and Four common DFNB loci in autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment in Markazi and Qom provinces of Iran. Iranian Journal of Biotechnology 2009;7:108–11.
14. Mahdieh N, Rabbani B, Shirkavand A, Bagherian H, Movahed ZS, Fouladi P, et al. Impact of consanguineous marriages in GJB2-related hearing loss in the Iranian population: a report of a novel variant. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 2011;15:489–93.


15. Hamid M, Karimipoor M, Chaleshtori MH, Akbari MT. A novel 355-357delGAG mutation and frequency of connexin-26 (GJB2) mutations in Iranian patients. J Genet 2009;88:359–62.


16. Azadegan-Dehkordi F, Bahrami T, Shirzad M, Karbasi G, Yazdanpanahi N, Farrokhi E, et al. Mutations in GJB2 as major causes of autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss: first report of c.299-300delAT mutation in Kurdish population of Iran. J Audiol Otol 2019;23:20–6.



17. Hashemi SB, Ashraf MJ, Saboori M, Azarpira N, Darai M. Prevalence of GJB2 (CX26) gene mutations in south Iranian patients with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Mol Biol Rep 2012;39:10481–7.


18. Esmaeili M, Bonyadi M, Nejadkazem M. Common mutation analysis of GJB2 and GJB6 genes in affected families with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss from Iran: simultaneous detection of two common mutations (35delG/del (GJB6-D13S1830)) in the DFNB1-related deafness. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2007;71:869–73.


19. Hosseinipour A, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M, Sasanfar R, Farhud D, Tolooi A, Doulati M, et al. Report of a new mutation and frequency of connexin 26 gene (GJB2) mutations in patients from three provinces of Iran. Iranian J Publ Health 2005;34:47–50.
20. Haghighat-Nia A, Keivani A, Nadeali Z, Fazel-Najafabadi E, Hosseinzadeh M, Salehi M. Mutation spectrum of autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss in central Iran. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2015;79:1892–5.


21. Koohiyan M, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M, Salehi M, Abtahi H, Reiisi S, Pourreza MR, et al. GJB2 mutations causing autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss (ARNSHL) in two Iranian populations: report of two novel variants. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2018;107:121–6.


22. Davarnia B, Babanejad M, Fattahi Z, Nikzat N, Bazazzadegan N, Pirzade A, et al. Spectrum of GJB2 (Cx26) gene mutations in Iranian Azeri patients with nonsyndromic autosomal recessive hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2012;76:268–71.


23. Zarepour N, Koohiyan M, Taghipour-Sheshdeh A, Nemati-Zargaran F, Saki N, Mohammadi-Asl J, et al. Identification and clinical implications of a novel MYO15A variant in a consanguineous Iranian family by targeted exome sequencing. Audiol Neurotol 2019;24:25–31.

24. Saadat M, Ansari-Lari M, Farhud DD. Consanguineous marriage in Iran. Ann Hum Biol 2004;31:263–9.


25. Ghasemnejad T, Shekari Khaniani M, Zarei F, Farbodnia M, Mansoori Derakhshan S. An update of common autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss genes in Iranian population. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2017;97:113–26.


26. Lucotte G, Diéterlen F. The 35delG mutation in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) associated with congenital deafness: European carrier frequencies and evidence for its origin in ancient Greece. Genet Test 2005;9:20–5.


27. Chaleshtori MH, Farhud DD, Patton MA. Familial and sporadic GJB2-related deafness in Iran: review of gene mutations. Iranian J Publ Health 2007;36:1–14.
28. Bonyadi M, Esmaeili M, Abhari M, Lotfi A. Mutation analysis of familial GJB2-related deafness in Iranian Azeri Turkish patients. Genetic Test Mol Biomarkers 2009;13:689–92.

29. Kalay E, Caylan R, Kremer H, de Brouwer AP, Karaguzel A. GJB2 mutations in Turkish patients with ARNSHL: prevalence and two novel mutations. Hear Res 2005;203:88–93.


30. Bazazzadegan N, Nikzat N, Fattahi Z, Nishimura C, Meyer N, Sahraian S, et al. The spectrum of GJB2 mutations in the Iranian population with non-syndromic hearing loss--a twelve year study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2012;76:1164–74.


31. Koohiyan M, Ahmadi A, Koohian F, Aghaei S, Amiri B, Hashemzadeh-Chaleshtori M. An update of spectrum and frequency of GJB2 mutations causing hearing loss in the south of Iran: a literature review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2019;119:136–40.


32. Sasanfar R, Tolouei A, Hoseinipour A, Farhud DD, Dolati M, Rad LH, et al. Frequency of a very rare 35delG mutation in two ethnic groups of Iranian populations. Iranian J Publ Health 2004;33:26–30.
33. Chaleshtori MH, Farrokhi E, Shahrani M, Kheiri S, Dolati M, Rad LH, et al. High carrier frequency of the GJB2 mutation (35delG) in the north of Iran. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2007;71:863–7.


34. Najmabadi H, Kahrizi K. Genetics of non-syndromic hearing loss in the Middle East. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2014;78:2026–36.


35. Chaleshtori MH, Farhud DD, Taylor R, Hadavi V, Patton MA, Afzal AR. Deafness-associated connexin 26 gene (GJB2) mutations in Iranian population. Iranian J Publ Health 2002;31:75–9.
36. Chaleshtori MH, Rad LH, Dolati M, Sasanfar R, Hoseinipour A, Zohour MM, et al. Frequencies of mutations in the connexin 26 gene (GJB2) in two populations of Iran (Tehran and Tabriz). Iranian J Publ Health 2005;34:1–7.
37. Maheshwari M, Vijaya R, Ghosh M, Shastri S, Kabra M, Menon PS. Screening of families with autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment (ARNSHI) for mutations in GJB2 gene: Indian scenario. Am J Med Genet A 2003;120A:180–4.


38. Minárik G, Ferák V, Feráková E, Ficek A, Poláková H, Kádasi L. High frequency of GJB2 mutation W24X among Slovak Romany (Gypsy) patients with non-syndromic hearing loss (NSHL). Gen Physiol Biophys 2003;22:549–56.

39. Salman M, Bashir R, Imtiaz A, Maqsood A, Mujtaba G, Iqbal M, et al. Mutations of GJB2 encoding connexin 26 contribute to non-syndromic moderate and severe hearing loss in Pakistan. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2015;272:2071–5.



40. Naghavi A, Nishimura C, Kahrizi K, Riazalhosseini Y, Bazazzadegan N, Mohseni M, et al. GJB2 mutations in Baluchi population. J Genet 2008;87:195–7.


41. Denoyelle F, Weil D, Maw MA, Wilcox SA, Lench NJ, Allen-Powell DR, et al. Prelingual deafness: high prevalence of a 30delG mutation in the connexin 26 gene. Hum Mol Genet 1997;6:2173–7.


42. Al-Achkar W, Al-Halabi B, Ali B, Moassass F. First report of prevalence c.IVS1+1G>A and del (GJB6-13S1854) mutations in Syrian families with non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2017;92:82–7.