 |
 |
- Search
| J Audiol Otol > Volume 19(3); 2015 > Article |
|
Abstract
The primary site of lesion induced by noise exposure is the hair cells in the organ of Corti and the primary neural degeneration occurs in synaptic terminals of cochlear nerve fibers and spiral ganglion cells. The cellular basis of noise-induced hearing loss is oxidative stress, which refers to a severe disruption in the balance between the production of free radicals and antioxidant defense system in the cochlea by excessive production of free radicals induced by noise exposure. Oxidative stress has been identified by a variety of biomarkers to label free radical activity which include four-hydroxy-2-nonenal, nitrotyrosine, and malondialdehyde, and inducible nitric oxide synthase, cytochrome-C, and cascade-3, 8, 9. Furthermore, oxidative stress is contributing to the necrotic and apoptotic cell deaths in the cochlea. To counteract the known mechanisms of pathogenesis and oxidative stress induced by noise exposure, a variety of antioxidant drugs including oxygen-based antioxidants such as N-acetyl-L-cystein and acetyl-L-carnitine and nitrone-based antioxidants such as phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone (PBN), disufenton sodium, 4-hydroxy PBN, and 2, 4-disulfonyl PBN have been used in our laboratory. These antioxidant drugs were effective in preventing or treating noise-induced hearing loss. In combination with other antioxidants, antioxidant drugs showed a strong synergistic effect. Furthermore, successful use of antioxidant drugs depends on the optimal timing of treatment and the duration of treatment, which are highly related to the time window of free radical formation induced by noise exposure.
Exposure to harmful noise at working places and military and recreational environments induces sensorineural hearing loss resulting from damages to cochlear and neural structures in the inner ear, called noise-induced hearing loss. Noise-induced hearing loss is classified into two types: chronic noise-induced hearing loss and acute acoustic trauma. Chronic noise-induced hearing loss refers to hearing impairment caused by continuous exposure to loud noise levels of 85 dB sound pressure level (SPL) and above for long periods of time while acute acoustic trauma represents hearing loss caused by short exposure to excessively loud sounds of 100 to 150 dB SPL [123]. Approximately 15 percent of American adults aging from 20 to 69 years old have noise-induced hearing loss [4]. Because noise-induced hearing loss is not necessarily painful or even annoying in spite of the high prevalence, it is called a hidden disorder by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [2].
Generally, hearing thresholds arrive at maximal increase immediately after noise exposure and gradually decrease for 3 weeks after noise exposure. After 3 weeks, they may fully recover (called temporary threshold shifts) or stabilize at an elevated value (called permanent threshold shifts) [5]. Temporary and permanent threshold shifts may occur from mechanical and metabolic damages induced by different noise exposure levels [156789]. Mechanical damages occur with exposure to the noise levels of 115-125 dB SPL while metabolic damages occur with exposure to the noise level of less than 115 dB SPL. Recent studies of noise-induced hearing loss show that temporary and permanent threshold shifts induced by noise exposure is primarily related to neural degeneration, called noise-induced neural degeneration. Noise-induced neural degeneration begins immediately after noise exposure and progresses for several years after the exposure [1011]. In addition, early exposure to noise can exacerbate age-related hearing loss as an evidence of a misspent youth, increase noise-induced hearing loss prevalence earlier in life, and accumulate its noxious effects over the course of a lifetime [11]. Primary noise-induced neural degeneration has been found in cochlear nerve peripheral terminals on inner hair cells and spiral ganglion cells in spite of clear recovery of cochlear thresholds and no loss of inner and outer hair cells (OHCs) [12].
Pharmacological interventions or approaches have been developed for the prevention or treatment of noise-induced neural degeneration using antioxidant drugs such as N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), acetyl-L-carnitine (ALCAR), phenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone (PBN), disufenton sodium (NXY-059), and 4-hydroxy PBN (4-OHPBN) [3612131415161718]. The therapeutic effects of antioxidant drugs on noise-induced neural degeneration is directly or indirectly associated with neural plasticity. Generally, neural plasticity refers to an ability of the brain and central nervous system to change and reorganize their structure and function in response to environmental cues, experience, learning, behavior, injury and/or diseases, and treatments. Neural degeneration related to deprivation of auditory system after noise exposure and neural plasticity associated with the use of antioxidant drugs are of particular interest because they provide valuable information of the rationale for one of the most promising treatment of noise-induced hearing loss. Our previous studies have demonstrated that antioxidant drugs can significantly attenuate the structural or functional consequences of noise trauma and rescue the cochlea and the central auditory system from their damages induced by noise trauma [36121314151617]. The present review explores the main damages and changes induced by noise exposure in the cochlea and the brain, the different role of each antioxidant drug in the treatment of noise-induced hearing loss, and the possible mechanisms and sites of action of each antioxidant drug alone and in combination with other antioxidant drugs for noise-induced hearing loss.
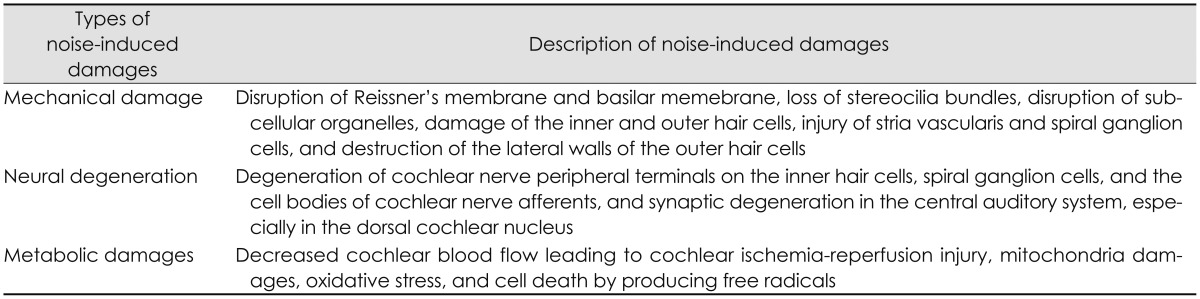
Many earlier studies of noise-induced trauma had demonstrated that there are mechanical damages of the anatomic and physiologic structures of the organ of Corti [91920]. Mechanical damages induced by noise exposure include the disruption of Reissner's membrane and basilar memebrane, loss of stereocilia bundles, disruption of subcellular organelles, damage of the inner and OHCs, injury of stria vascularis and spiral ganglion cells, and destruction of the lateral walls of the OHCs [789]. Among these damages, the primary site of lesion is the hair cells in the organ of Corti [192021]. Loss of hair cells was found in minutes to hours after noise exposure while loss of spiral ganglion cells was not observed for weeks to months after noise exposure [19]. It is called a secondary neural degeneration due to the neural degeneration occurring secondary to the hair cell loss. However, recent studies have showed that noise exposure can induce hearing loss without any mechanical damages of the organ of Corti. Noise-induced permanent threshold shifts do not require hair-cell loss but can occur with stereocilia damage alone [20]. In spite of noise exposure, it has been observed that the organ of Corti was intact and there were no hair cell loss outside of the extreme high-frequency end of the cochlear spiral and no pathologic change in other cochlear structures such as the stria vascularis, spiral limbus, and tectorial membranes [11]. The most distinct pathological site for noise-induced hearing loss was within the spiral ganglion cells, the cell bodies of cochlear nerve afferents [511]. There were a rapid and irreversible loss of cochlear nerve peripheral terminals on hair cells and a slow degeneration of spiral ganglion cells after noise exposure [21]. Because the neural loss was not associated with hair cell loss, it is considered a "primary" neural degeneration rather than occurring secondary to the hair cell degeneration [5]. In addition, noise-induced loss of spiral ganglion cells is delayed by months and can progress for years after noise exposure [511]. These findings contrast with the common notions of noise-induced trauma that noise induced threshold shifts increase only as long as the noise exposure continues, asymptote to permanently stable levels within 2-4 weeks after exposure, and initiate a recovery immediately after exposure termination [10].
The primary neural degeneration induced by noise exposure was shown in widespread and severe swelling of the synaptic terminals of cochlear nerve fibers of ears in a variety of mammals such as cat, guinea pig, and mouse [212223]. The acute swelling of afferent terminals represents a type of glutamate excitotoxicity occurring in the inner and OHCs [5]. Although the exact timing of degeneration and regeneration after excitotoxicity is not clearly identified, excitotoxic swelling was observed within 24-48 h after exposure and absent more than 1 week after exposure [212223]. Another study showed that most terminals degenerate after noise exposure and then regenerate within a few (<5) days to re-innervate the hair cells [24]. Loss of spiral ganglion cells representing the synaptic degeneration was not recovered by 8 weeks after exposure and required 2 years to approach the 50% cell loss [22]. When noise-induced neural degeneration can be spontaneously recovered is of clinically fundamental importance to the development of pharmacological treatments for noise-induced hearing loss.
As a result of noise exposure, synaptic degeneration and neural plasticity were found in the central auditory system, especially in the dorsal cochlear nucleus (DCN). Pathological changes induced by noise exposure in the central auditory system have been identified by many studies. The number or density of axons was reduced by half in the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN) [25] and degeneration of synapsing nerve endings of secondary neurons was seen in the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus and octopus cell area of the PVCN [26]. Neuropil volume and neuron size were decreased and neuronal packing density with minimal changes in neuron number was increased in the VCN and deep layer of the DCN receiving the heaviest input from cochlear afferents [26]. Cytological changes and degeneration of synaptic endings in the cochlear nucleus were found within 1-16 weeks after noise exposure and these changes progressed to mitochondrial disintegration and overt watery degeneration [27]. The long-term effects of noise exposure for periods of 6 and 8 months after nose exposure were also observed on the fine structure of synaptic endings in the cochlear nucleus, especially in the neuropil and the synapses on the globular bushy cell, which form part of the main ascending auditory pathway [27]. This indicates that noise-induced hearing loss may progress as a neurodegenerative disease with the capacity for synaptic reorganization within the cochlear nucleus. Substantial losses of axons and synaptic terminals with excitatory and inhibitory cytology were seen in the PVCN after 1 week, progressed for 16-24 weeks after exposure, and fully recovered by 24-32 weeks after noise exposure [28]. Neural plasticity in the DCN induced by noise exposure can be evaluated by synapse biomarkers such as synaptophysin and precerebellin. Synaptophysin is a biomarker for synaptic reorganization after denervation and quantification of synapses and widely found in presynaptic membranes and vesicles [29]. Precerebellin (Cbln1) is the precursor of the brain-specific neuropeptide cerebelin and a synapse organizer for both pre- and post-synaptic components [17]. Cbln1 is involved for synaptic integrity, plasticity as well as synapse maintenance in the cerebellum [17]. Decreased synaptophysin and precerebellin expressions and selective denegeration of nerve terminals surrounding cartwheel cells and their primary dendrites were found in the middle region of the DCN after noise exposure [17]. In spite of these previous studies, the mechanisms involved in synaptic degeneration and plasticity of the central auditory system induced by noise exposure are not clear.
On the other hand, the cochlea is a highly metabolically active sensory organ which receives 0.5 mL per minute of blood flow in normal conditions [8]. Metabolically, noise exposure can decrease cochlear blood flow leading to cochlear ischemia-reperfusion injury, induce cell death by producing free radicals, and contribute to injury and deaths of hair cells and spiral ganglion cells [178]. This process in the cochlea is very similar to that occurring in the brain in response to a stroke. In metabolic damages induced by noise exposure, oxidative stress plays a major role in understanding the basic mechanisms of noise-induced cochlear injury and developing effective pharmarcological protection and treatment strategies. Oxidative stress refers to a severe disruption in the balance between the production of free radicals and antioxidant defense system in the cochlea by excessive production of free radicals induced by noise exposure [30]. Free radicals are any atoms, molecules, or ions with an unpaired electron making them highly active with cellular proteins, membrane lipids, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and cellular organelles [30]. Free radicals consist of reactive oxygen species (ROS) containing at least one molecule of oxygen such as superoxide (O2), hydroxyl (OH), peroxyl (RO2), alkoxyl (RO), and hydroperoxyl (HO2) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) containing at least one molecule of nitrogen such as nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) [130]. Possible mechanisms and sites of action of oxidative stress induced by noise exposure within the cochlea are ischemia-reperfusion injury in the stria vascularis, excessive glutamate release at the afferent synapse of the inner and OHCs, mitochondrial injury associated with excessive production of ROS and RNS in hair cells, depletion of glutathione within the OHCs, and increases in intracellular calcisum in hair cells [8]. In addition, noise-induced oxidative stress makes changes to antioxidant enzymes, and lipid peroxidation in the spiral ganglion, organ of Corti, and stria vascularis and leads to oxidation of actin filaments of stereocilia and cell membrane lipid, protein oxidation, damage to nuclear DNA, damage to mitochondrial DNA, swelling and degeneration of afferent nerve endings, and release of toxins such as 4-hydroxy 2, 3-nonenal [hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE), an aldehyde adduct of membrane lipid peroxidation] [18]. The entire damages induced by noise exposure are summarized as shown in Table 1.
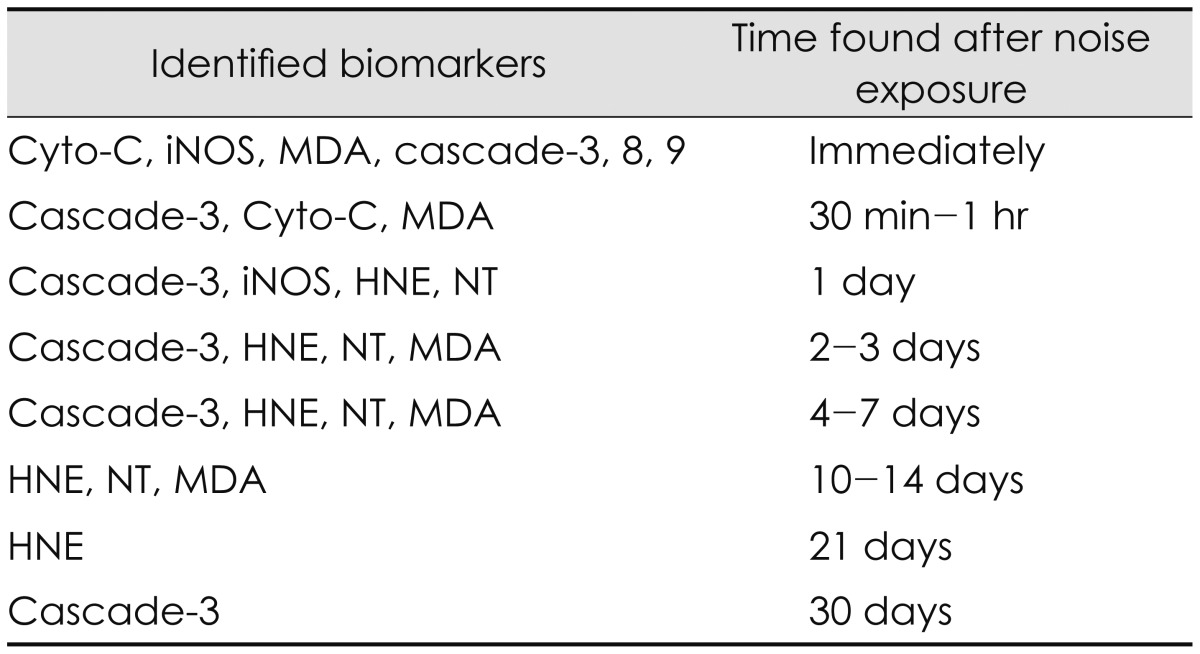
Oxidative stress has been identified by a variety of biomarkers to label ROS and RNS activity in the cochlea and the brain [16]. These biomarkers include 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (4-HNE), nitrotyrosine (NT), and malondialdehyde (MDA), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cytochrome-C, and cascade-3, 8, 9. 4-HNE is a biomarker which indicates oxidative damage formed as an abundant product of polyunsaturated fatty acid oxidation and decomposition, responds extensively to DNA and proteins, reduces intracellular glutathione, and modifies many cell signaling cascades [1617]. Delayed 4-HNE formation was observed in at the lateral wall and Claudius cells on days 1-2, at the Deiter's cells on days 3, at the outer hair cell bodies on 7-10 days and 14-21 days after noise exposure [15163132]. NT is a biomarker of NO production which formed by nitration of a tyrosine residue in proteins [15]. NT formation was also found in the hair cells on 1 day as well as 7 to 21 days after noise exposure [15163132]. MDA, another free radical biomarker and an end product of lipid peroxidation represents an early common stage in the peroxidative process and was observed in cochlea immediately after noise exposure as well as a second peak at 12 days [15]. The expression of iNOS in the wall of the blood vessels of stria vascularis and marginal cells was observed after noise exposure [33]. In more detail, strong iNOS expression was observed in the hair cells and the stria vascularis marginal cells immediately after noise exposure while week iNOS expression was found in the vascular endothelium, marginal cells, nerve fibers, stereocilia of hair cells and Hensen's cells of the organ of Corti on 1 day after noise exposure [34]. Furthermore, noise exposure induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria and caspase-3, -8, or -9 [35]. The cytochrome c release took place in both apoptotic and necrotic OHCs while caspase activation occurred only in the apoptotic OHCs and not in the necrotic OHCs [35]. Another biomarker, c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase plays an important role in a mitochondrial cell death pathway and remains in cochlear tissues for as long as 3 weeks after noise exposure [36]. In summary, oxidative stress identified by biomarkers can occur immediately after noise exposure and progress up to 30 days after noise exposure [73132]. Of days after noise exposure, the first 10 days are the most important time period for free radical formation because the formation of free radicals reaches their peaks [3132]. A variety of biomarkers identified in the cochlea and the brain for noise-induced hearing loss and their time found after noise exposure are listed as shown in Table 2.
Noise-induced oxidative stress can directly or indirectly contribute to cell death in the cochlea. A clear understanding of the biological steps in cell death may lead to the development of pharmacological interventions for prevention and treatment of noise-induced hearing loss [7]. Cell death induced by acoustic overexposure occurs through three different pathways. The primary cell death pathway is apoptosis, an active programmed cell death which is marked as shrunken dark cytoplasm with a pyknotic nucleus, remaining intact cell membrane with no inflammatory response [7]. This apoptosis can be mediated by the activity of enzymes (caspase-3, -8, -9), cytochrome-C, c-Jun, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase [83536]. The second cell death pathway is necrosis, a passive unprogrammed cell death which is identified by swollen and pale-staining cytoplasm resulting in rupture of the cell, spillage of the cell contents, damage to surrounding tissue, and evocation of an inflammatory response [7]. The third cell death pathway is relatively a newly defined one, which is characterized by no basolateral plasma membrane but cellular debris arranged in the shape of an intact outer hair cell with a nucleus deficient in nucleoplama [20]. The necrotic and apoptotic pathways were observed in the cochlea immediately after noise exposure [37]. As time passed, the necrotic death disappeared and the apoptotic pathway is more responsible for the cell death.
Pharmacological approaches to prevent or treat noise-induced hearing loss have been developed by increasing the antioxidant defense system or reducing the oxidative stress in the cochlea. To maximize the therapeutic effects, they need to be designed to counteract the known mechanisms of pathogenesis induced by noise exposure such as mitochondrial injury, glutamate excitotoxicity, glutathione depletion, excessive increases in intracellular calcium fluxes, and ischemiareperfusion mentioned in the preceding section [8]. A variety of antioxidant drugs have been used for prevention and treatment of noise-induced hearing loss. Antioxidant drugs used in our laboratory are classified into two different types: oxygen-based and nitrone-based antioxidant drugs [1368121315161718].
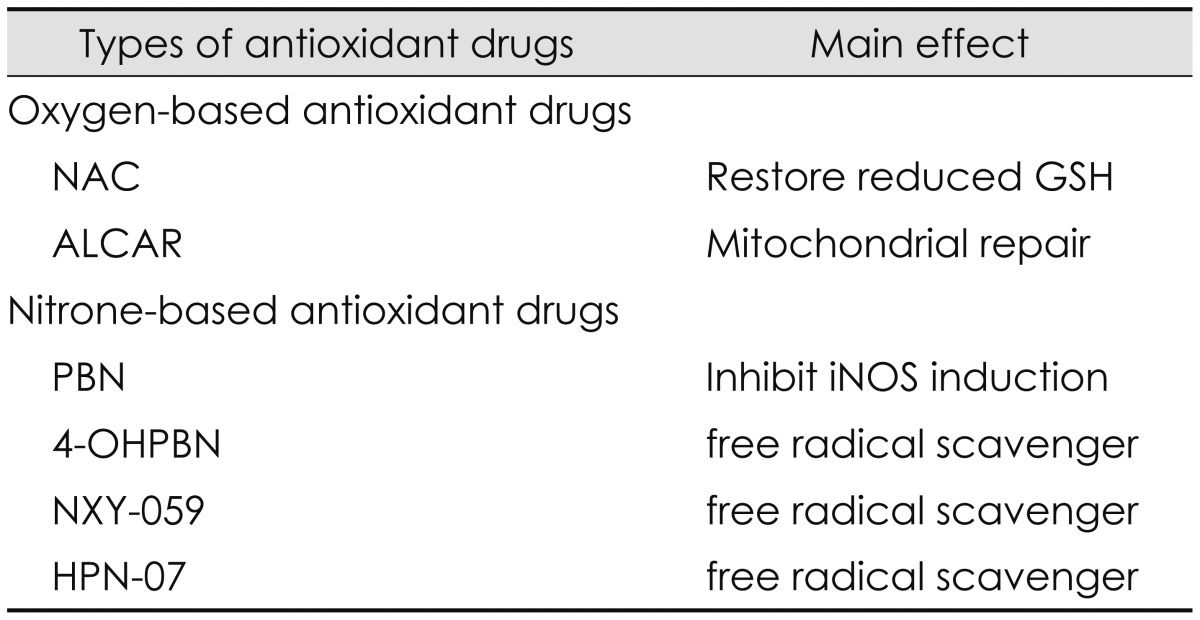
Oxygen-based antioxidant drugs have been developed to inhibit the excessive production of ROS induced by noise exposure. They include NAC and ALCAR. Generally, NAC has been used as an antioxidant precursor to glutathione in the treatment of a variety of diseases including paracetamol overdose, human immunodeficiency virus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, contrast-induced nephropathy, brain disorders, and Alzheimer disease [8]. NAC has also been used to prevent or treat noise-induced hearing loss because it functions as ROS scavenger and as a neuroprotective agent by mainly replenishing glutathione in the face of oxidative stress, decreasing mitochondrial injury, caspase, mitogen-activated protein kinase/c-Jun kinase, and Src protein tyrosine kinase activation as well as reducing glutamate excitotoxicity, lipid peroxidation, cell death, and inflammation [16838394041]. NAC significantly decreased permanent threshold shifts and hair cell loss induced by noise exposure and the therapeutic effects were greater in combination with other antioxidant drugs or at higher doses or when used for a long period of time after noise exposure [36154041]. Generally, ALCAR has been used in the treatments of dementia, Parkinson's disease, neuropathic pain, and alcohol-induced oxidative damage in the brain [38394041]. ALCAR has major functions to prevent mitochondrial injury resulting from either overproduction of ROS or other damage such as glutamate excitoxicity, ischemia-reperfusion, or glutathione depletion by oxidative stress, restore mitochondrial efficiency with a consistent reduction of mitochondrial free radical formation, and reduce mitochondrial-induced apoptosis by maintaining mitochondrial bioenergetics [838394041]. Permanent threshold shifts for NAC and ALCAR were significantly reduced at 1 h and 4 h after noise exposure but not significantly reduced at 12 h after noise exposure [38]. The reduced amount for NAC was 15.5, 20.2, and 27.4 dB SPL at 1, 4, and 12 h after noise exposure, respectively while that of ALCAR was 14.4, 17.5, and 30.7 dB SPL at 1, 4, and 12 h after noise exposure, respectively.
Nitrone-based antioxidant drugs have been developed to reduce the over-production of RNS induced by noise exposure [61542]. Nitrone-based antioxidant drugs include a PBN family such as PBN, NXY-059, 4-OHPBN, and 2, 4-disulfonyl PBN (HPN-07). Historically, nitrones were first used to trap free radicals in chemical and biochemical systems of many animal models for the treatment of stroke in the mid-1970s [1442]. Then the use of nitrones as potential pharmaceutical agents has been extended to a variety of diseases such as neural damage, toxin-induced brain seizures, bacterial meningitis, cancer development, Parkinson disease, and Alzheimer disease [1442]. In diverse animal models, PBN has been known as a nitrone-based spin trapping agent of free radical species such as hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anions [6]. PBN plays its main roles as a neuroprotective agent by reducing oxidative stress and restoring antioxidant defense system [6] and a potent anti-inflammatory agent by inhibiting the activation/mRNA level of inflammatory mediators such as iNOS, inducible cyclooxygenase (COX2), COX catalytic activity, and nuclear factor kappaB [6]. PBN was effective in protecting cochlea from damages induced by combined exposure of noise and industrial chemicals such as carbon monoxide and acrylonitrile. It has been known that carbon monoxide can damage type I spiral ganglion synapse of the inner hair cell functioning as a glutamate neurotransmitter [43] while acrylonitrile can deplete glutathione by decreasing reactive epoxide binding to cytochrome-C oxidase [44]. A novel PBN derivative, 2, 4-disulfophenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone, referred to as NXY-059 was commercially developed for treatment of acute ischemic stroke [45]. NXY-059 was also a free radical trap and developed to overcome the limitation of PBN showing the short window of opportunity for administration. However, NXY-059 was not significantly effective in treating acute ischemic stroke. It has been known that 4-OHPBN is a nitrone-based free radical trap and an inhibitor of iNOS [16]. When a major metabolite of PBN, 4-OHPBN was used in the choline-deficiency amino acid defined diet, it showed strong anti-cancer activity [14]. Applied to the treatment of noise-induced hearing loss, 4-OHPBN alone and in combination with other oxygen-based antioxidant drugs were effective in making significant reduction in both permanent hearing threshold shifts and outer hair cell loss [6]. Compared to PBN and its other derivatives including 3-hydroxyl PBN, 2-hydroxyl PBN, and 2-sulfoxy PBN, 4-OHPBN showed stronger effect on suppressing hepatocarcinogenesis than the parent PBN and other derivatives [6]. Recently, another free radical spin trap reagent, disodium 2, 4-disulfophenyl-N-tertbutylnitrone, referred to as HPN-07, in combination of NAC has been tested as a therapeutic approach for noise-induced hearing loss [18]. The combination of HPN-07 and NAC was effective in reducing permanent threshold shifts and protecting cochlear sensory cells and afferent neuritis from cochlear damage induced by noise exposure [18]. These antioxidant drugs and their main effects are summarized as shown in Table 3.
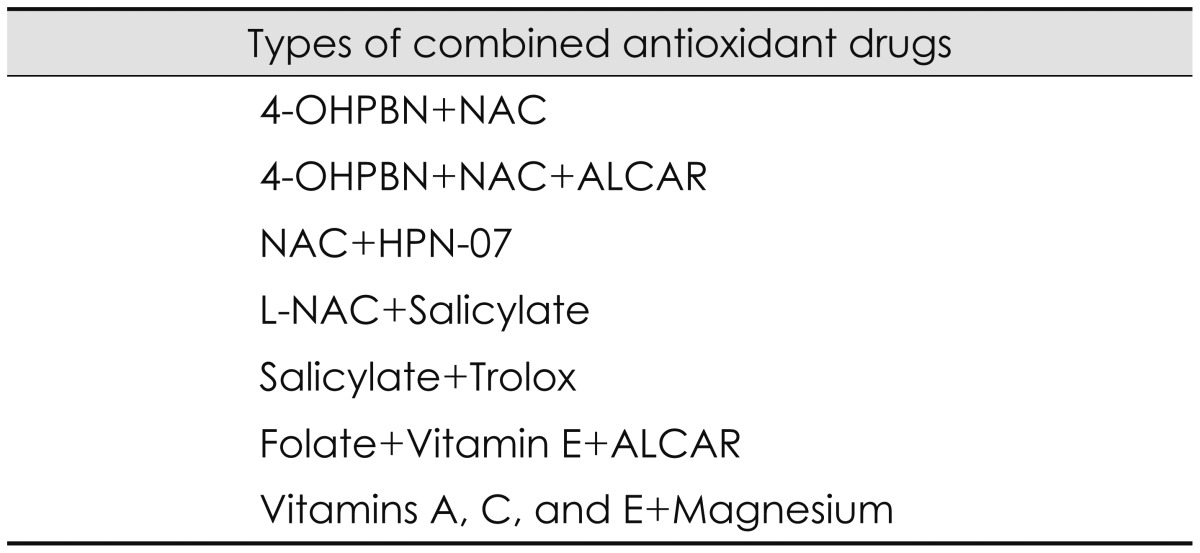
Since each antioxidant drug has different mechanisms and specific sites of action, there is a strong synergistic effect in combination with other antioxidant drugs. The synergistic effect was tested with a variety of combinations in our studies. The combination of 4-OHPBN and NAC administered by intraperitoneal injection decreased permanent threshold shifts by 75% while another combination of 4-OHPBN and NAC and ALCAR reduced permanent threshold shifts by 91% compared to 4-OHPBN alone [3]. The combination of antioxidant drugs showed greater efficacy and required lower dosages than each antioxidant drug. The combination of 4-OHPBN and NAC administered by oral injection had greater therapeutic effects than the intraperitoneally administered 4-OHPBN alone [3]. When the initial treatment was delayed up to 1-2 days after noise exposure and the duration of treatment was extended over the period of 7-10 days after noise exposure, the synergistic effect of the combination of 4-OHPBN and NAC and ALCAR was observed [15]. The combination of 4-OHPBN and NAC and ALCAR restored the expressions of synaptic biomarkers such as synaptophysin and precerebellin in the DCN [17]. The combination of NAC and HPN-07 inhibited the upregulation of c-fos expression in the dorsal and ventral cochlear nucleus after noise exposure [18]. In addition, the combination of antioxidant drugs could expand the therapeutic time window for noise-induced hearing loss [16]. The synergistic effect of combination of antioxidant drugs has been proven by many other studies. The combination of N-L-acetylcystein (L-NAC) and salicylate administered by oral injection was effective in either preventing or attenuating noise-induced hearing loss [46]. Salicylate is a hydroxyl radical scavenger, an inhibitor of the transcription factor nuclear factor-╬║B, a potential activator of inflammatory or cell death pathways, and a cochlear protectant from cell death [46]. The combination of salicylate and trolox significantly decreased auditory brainstem response deficits and ROS/RNS production and reduced hair cell damage [32]. Trolox is a water-soluble analog of alpha-tocopherol and an inhibitor of peroxynitrite-mediated tyrosine and guanine nitrosylation [32]. The combination of folate, vitamin E, and ALCAR provided superior protection against oxidative stress induced by noise exposure to that derived from each agent alone [47]. Folate is known to maintain levels of the endogenous antioxidant glutathione while vitamin E functions to prevent oxidative damage induced by noise exposure [47]. Another combination of vitamins A, C, and E plus magnesium showed strong protection of neurodegenerative cell death induced by noise exposure [48]. Vitamin A is a scavenger of ROS and vitamin C has been used to detoxify free radicals [48]. Vitamin E is an inhibitor of lipid peroxidation which is found in cell membranes while magnesium plays an important role to reduce vasoconstriction occurring with ROS production [48]. These studies on any combination of antioxidant drugs demonstrates that there are considerable differences in the therapeutic effect of each antioxidant drug and strong synergistic effects of antioxidant drugs because noise induced hearing loss result from a variety of damage pathways and each antioxidant drug targets different mechanisms and sites of action. Various combination of antioxidant drugs are listed as shown in Table 4.
Success of pharmacological intervention for prevention and treatment of noise-induced hearing loss depends on the time of treatment/initial treatment and the duration of treatment after noise exposure. Antioxidant drugs administered shortly before noise exposure (pre-treatment) decreased permanent threshold shifts and hair cells by approximately 75% and over 50%, respectively [46]. These results are consistent with other studies used other antioxidant drugs [6]. Antioxidant drugs administered after noise exposure (post-treatment) significantly reduced permanent threshold shifts [36121516171838394041]. However, post-treatment of antioxidant drugs (LNAC and salicylate) showed no protection from noise-induced hair cell loss [46]. This may indicate special cases that noise-induced hair cell loss is not directly associated with the auditory permanent threshold shifts. Furthermore, proper timing of initial treatment is clinically important information to maximize the effect of antioxidant drugs. Given 1 h after noise exposure, antioxidant drugs showed the greatest reduction in permanent threshold shifts and hair cell loss while the same drugs initially administered at 4 h after noise exposure were still effective in reducing noise-induced hearing loss [39]. However, no efficacy was found in the drugs initially administered at 12 h after noise exposure [39]. This suggests that the initial administration as 12 h after noise exposure is too late to counteract noise-induced cochlear damage. In previous studies of pharmacological intervention for noise-induced hearing loss, the treatment lasted for 3 days after noise exposure. However, it was observed that free radical formation after noise exposure was low initially, reached a maximum at 7 to 10 days, and then declined, referred to as a secondary oxidative burst [31]. When the duration of treatment was extended up to 10 days after noise exposure to counteract the secondary oxidative burst, antioxidant drugs were effective in treating noise-induced hearing loss [15]. In addition, when the duration of treatment was combined with treatment delay (initial injections starting 24 h to 48 h after noise exposure), maximal decreases in permanent threshold shifts and hair cell loss were found in experimental groups treated 9 days with initial injection starting 24 h after noise exposure [15]. This indicates that when the duration of treatment increases from 3 days to 8/9 days, antioxidant drugs are still effective in treating noise-induced hearing loss in spite of the treatment delay. The optimal timing and duration of treatment for noise-induced hearing loss is highly related to the temporal formation of free radicals after noise exposure. Therefore, best treatment strategies of antioxidant drugs for noise-induced hearing loss should be established on basis of the time window of free radical generation after noise exposure and the unique mechanisms and sites of action of each antioxidant drug.
This study reviewed structural and functional changes and basic mechanisms induced by noise exposure in the cochlea and the brain and the therapeutic effects of a variety of antioxidant drugs which have been used in our laboratory for treatment of noise-induced hearing loss. Main molecular/cellular changes induced by noise exposure are summarized in oxidative stress, which caused by excessive production of free radicals consisting of ROS and RNS and contributes to cell death in the cochlea. To decrease the oxidative stress induced by noise exposure, a variety of antioxidant drugs have been used in our laboratory. They include oxygen-based antioxidant such as NAC and ALCAR and nitrone-based antioxidants such as PBN, NXY-059, 4-OHPBN, and HPN-07. Each antioxidant drug has unique mechanisms and specific sites of action. There is a strong synergistic effect when each antioxidant is used in combination with other antioxidants. The study demonstrates that successful use of antioxidant drugs depends on the optimal timing of treatment and the duration of treatment, which may be highly associated with the time window of free radical formation induced by noise exposure. However, since the clear relationship between free radical formation and the optimal timing of antioxidant treatment was not found yet, further research are required.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2012R1A1A4A01017139).
References
2. Choi CH. Hearing threshold shift and speech intelligibility index of personal hearing protective devices. Audiology 2013;9:74ŌĆō79.

3. Choi CH, Du X, Floyd RA, Kopke RD. Therapeutic effects of orally administrated antioxidant drugs on acute noise-induced hearing loss. Free Radic Res 2014;48:264ŌĆō272. PMID: 24182331.


4. National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Noise induced hearing loss cited 2015 Aug 15. Available from: http://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hearing/pages/noise.aspx.
5. Kujawa SG, Liberman MC. Adding insult to injury: cochlear nerve degeneration after "temporary" noise-induced hearing loss. J Neurosci 2009;29:14077ŌĆō14085. PMID: 19906956.



6. Choi CH, Chen K, Vasquez-Weldon A, Jackson RL, Floyd RA, Kopke RD. Effectiveness of 4-hydroxy phenyl N-tert-butylnitrone (4-OHPBN) alone and in combination with other antioxidant drugs in the treatment of acute acoustic trauma in chinchilla. Free Radic Biol Med 2008;44:1772ŌĆō1784. PMID: 18328271.


7. Henderson D, Bielefeld EC, Harris KC, Hu BH. The role of oxidative stress in noise-induced hearing loss. Ear Hear 2006;27:1ŌĆō19. PMID: 16446561.


8. Kopke RD, Coleman JKM, Liu J, Jackson RL, Van De Water TR. Mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss and otoprotective strategies. In: Van De Water TR, Staecker H. editors. Otolaryngology: basic science and clinical review. New York: Thieme;2006. p.395ŌĆō408.
9. Le Prell CG, Yamashita D, Minami SB, Yamasoba T, Miller JM. Mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss indicate multiple methods of prevention. Hear Res 2007;226:22ŌĆō43. PMID: 17141991.



10. Miller JD, Watson CS, Covell WP. Deafening effects of noise on the cat. Acta OtoLaryngol Suppl 1963;176:1ŌĆō91.
11. Kujawa SG, Liberman MC. Acceleration of age-related hearing loss by early noise exposure: evidence of a misspent youth. J Neurosci 2006;26:2115ŌĆō2123. PMID: 16481444.



12. Choi CH. Therapeutic effect of combined antioxidant drugs (4-OHPBN plus NAC) on acute acoustic trauma in terms of distortion product otoacoustic emission. Audiology 2011;7:51ŌĆō59.

13. Choi CH. Preliminary study of the therapeutic effect of a nitronebased antioxidant drug (HPN-07) on acute acoustic trauma. Korean J Commun Disord 2011;16:202ŌĆō210.
14. Floyd RA, Kopke RD, Choi CH, Foster SB, Doblas S, Towner RA. Nitrones as therapeutics. Free Radic Biol Med 2008;45:1361ŌĆō1374. PMID: 18793715.



15. Choi CH, Chen K, Du X, Floyd RA, Kopke RD. Effects of delayed and extended antioxidant treatment on acute acoustic trauma. Free Radic Res 2011;45:1162ŌĆō1172. PMID: 21756051.


16. Du X, Choi CH, Chen K, Cheng W, Floyd RA, Kopke RD. Reduced formation of oxidative stress biomarkers and migration of mononuclear phagocytes in the cochleae of chinchilla after antioxidant treatment in acute acoustic trauma. Int J Otolaryngol 2011;2011:612690PMID: 21961007.



17. Du X, Chen K, Choi CH, Li W, Cheng W, Stewart C, et al. Selective degeneration of synapses in the dorsal cochlear nucleus of chinchilla following acoustic trauma and effects of antioxidant treatment. Hear Res 2012;283:1ŌĆō13. PMID: 22178982.


18. Lu J, Li W, Du X, Ewert DL, West MB, Stewart C, et al. Antioxidants reduce cellular and functional changes induced by intense noise in the inner ear and cochlear nucleus. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2014;15:353ŌĆō372. PMID: 24497307.



19. Spoendlin H. Primary structural changes in the organ of Corti after acoustic overstimulation. Acta Otolaryngol 1971;71:166ŌĆō176. PMID: 5577011.


20. Bohne BA, Harding GW, Lee SC. Death pathways in noise-damaged outer hair cells. Hear Res 2007;223:61ŌĆō70. PMID: 17141990.


21. Liberman MC, Beil DG. Hair cell condition and auditory nerve response in normal and noise-damaged cochleas. Acta Otolaryngol 1979;88:161ŌĆō176. PMID: 495068.


22. Liberman MC, Mulroy MJ. Acute and chronic effects of acoustic trauma: cochlear pathology and auditory nerve pathophysiology. In: Hamernik RP, Henderson D, Salvi R. editors. New perspectives on noise-induced hearing loss. New York: Raven Press;1982. p.105ŌĆō136.
23. Wang Y, Hirose K, Liberman MC. Dynamics of noise-induced cellular injury and repair in the mouse cochlea. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2002;3:248ŌĆō268. PMID: 12382101.



24. Pujol R, Puel JL. Excitotoxicity, synaptic repair, and functional recovery in the mammalian cochlea: a review of recent findings. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999;884:249ŌĆō254. PMID: 10842598.


25. Bilak M, Kim J, Potashner SJ, Bohne BA, Morest DK. New growth of axons in the cochlear nucleus of adult chinchillas after acoustic trauma. Exp Neurol 1997;147:256ŌĆō268. PMID: 9344551.


26. Theopold HM. Degenerative alterations in the ventral cochlear nucleus of the guinea pig after impulse noise exposure. A preliminary light and electron microscopic study. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 1975;209:247ŌĆō262. PMID: 175774.


27. Kim JJ, Gross J, Potashner SJ, Morest DK. Fine structure of degeneration in the cochlear nucleus of the chinchilla after acoustic overstimulation. J Neurosci Res 2004;77:798ŌĆō816. PMID: 15334599.


28. Kim JJ, Gross J, Potashner SJ, Morest DK. Fine structure of longterm changes in the cochlear nucleus after acoustic overstimulation: chronic degeneration and new growth of synaptic endings. J Neurosci Res 2004;77:817ŌĆō828. PMID: 15334600.


29. Benson CG, Gross JS, Suneja SK, Potashner SJ. Synaptophysin immunoreactivity in the cochlear nucleus after unilateral cochlear or ossicular removal. Synapse 1997;25:243ŌĆō257. PMID: 9068122.


30. Evans P, Halliwell B. Free radicals and hearing. Cause, consequence, and criteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999;884:19ŌĆō40. PMID: 10842581.


31. Yamashita D, Jiang HY, Schacht J, Miller JM. Delayed production of free radicals following noise exposure. Brain Res 2004;1019:201ŌĆō209. PMID: 15306254.


32. Yamashita D, Jiang HY, Le Prell CG, Schacht J, Miller JM. Post-exposure treatment attenuates noise-induced hearing loss. Neuroscience 2005;134:633ŌĆō642. PMID: 15961244.


33. Shi X, Nuttall AL. Upregulated iNOS and oxidative damage to the cochlear stria vascularis due to noise stress. Brain Res 2003;967:1ŌĆō10. PMID: 12650960.


34. Shi X, Dai C, Nuttall AL. Altered expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in the cochlea. Hear Res 2003;177:43ŌĆō52. PMID: 12618316.


35. Nicotera TM, Hu BH, Henderson D. The caspase pathway in noiseinduced apoptosis of the chinchilla cochlea. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2003;4:466ŌĆō477. PMID: 14534835.



36. Wang J, Ruel J, Ladrech S, Bonny C, van de Water TR, Puel JL. Inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase-mediated mitochondrial cell death pathway restores auditory function in sound-exposed animals. Mol Pharmacol 2007;71:654ŌĆō666. PMID: 17132689.


37. Hu BH, Henderson D, Nicotera TM. Involvement of apoptosis in progression of cochlear lesion following exposure to intense noise. Hear Res 2002;166:62ŌĆō71. PMID: 12062759.


38. Coleman JK, Kopke RD, Liu J, Ge X, Harper EA, Jones GE, et al. Pharmacological rescue of noise induced hearing loss using N-acetylcysteine and acetyl-L-carnitine. Hear Res 2007;226:104ŌĆō113. PMID: 17023129.


39. Kopke RD, Coleman JK, Liu J, Campbell KC, Riffenburgh RH. Candidate's thesis: enhancing intrinsic cochlear stress defenses to reduce noise-induced hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2002;112:1515ŌĆō1532. PMID: 12352659.


40. Kopke R, Bielefeld E, Liu J, Zheng J, Jackson R, Henderson D, et al. Prevention of impulse noise-induced hearing loss with antioxidants. Acta Otolaryngol 2005;125:235ŌĆō243. PMID: 15966690.


41. Kopke RD, Jackson RL, Coleman JK, Liu J, Bielefeld EC, Balough BJ. NAC for noise: from the bench top to the clinic. Hear Res 2007;226:114ŌĆō125. PMID: 17184943.


42. Floyd RA, Castro Faria Neto HC, Zimmerman GA, Hensley K, Towner RA. Nitrone-based therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases: their use alone or in combination with lanthionines. Free Radic Biol Med 2013;62:145ŌĆō156. PMID: 23419732.



43. Fechter LD, Chen GD, Rao D, Larabee J. Predicting exposure conditions that facilitate the potentiation of noise-induced hearing loss by carbon monoxide. Toxicol Sci 2000;58:315ŌĆō323. PMID: 11099644.


44. Fechter LD, Gearhart C, Shirwany NA. Acrylonitrile potentiates noise-induced hearing loss in rat. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2004;5:90ŌĆō98. PMID: 14669069.



45. Maples KR, Green AR, Floyd RA. Nitrone-related therapeutics: potential of NXY-059 for the treatment of acute ischaemic stroke. CNS Drugs 2004;18:1071ŌĆō1084. PMID: 15581379.


46. Kopke RD, Weisskopf PA, Boone JL, Jackson RL, Wester DC, Hoffer ME, et al. Reduction of noise-induced hearing loss using LNAC and salicylate in the chinchilla. Hear Res 2000;149:138ŌĆō146. PMID: 11033253.


47. Dhitavat S, Ortiz D, Rogers E, Rivera E, Shea TB. Folate, vitamin E, and acetyl-L-carnitine provide synergistic protection against oxidative stress resulting from exposure of human neuroblastoma cells to amyloid-beta. Brain Res 2005;1061:114ŌĆō117. PMID: 16256963.


48. Le Prell CG, Hughes LF, Miller JM. Free radical scavengers vitamins A, C, and E plus magnesium reduce noise trauma. Free Radic Biol Med 2007;42:1454ŌĆō1463. PMID: 17395018.