 |
 |
- Search
| J Audiol Otol > Volume 22(2); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Objectives
Changes in distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) caused by contralateral suppression (CS) allow the function of the auditory efferent system to be evaluated. Parameters affording maximum CS are preferred in terms of clinical application. Our objective was to evaluate the effects of primary levels and frequencies on DPOAE-mediated CS.
Subjects and Methods
Sixteen subjects with normal hearing participated. DPOAEs were recorded with and without contralateral acoustic stimulation; we delivered broadband noise of 65 dB SPL at f2 frequencies between 1,000 Hz and 6,727 Hz, at 8 pt/octave. The L2 was varied between 40 dB SPL and 80 dB SPL in 10-dB steps.
Results
L2 did not significantly affect DPOAE-mediated CS. Higher L2 levels significantly reduced the fine structure depth of both the baseline and suppressed DPOAE datasets. The amount of CS was greatly affected by the f2 frequency; lower and higher frequency ranges afforded significantly stronger suppression than did mid-frequencies within the studied range.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest that DPOAE CS should be measured over a wide range of frequencies as the amount of CS seems to be highly dependent on f2. The use of a higher L2 level may be optimal when it is sought to evoke strong DPOAE-mediated suppression while simultaneously minimizing DPOAE fine structure. Our findings may assist in optimization of clinical procedures evaluating the integrity of the auditory efferent system.
Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs) are low-intensity acoustic sounds originating in the cochlea secondary to the movement of cochlear hair cells following external acoustic stimulation [1]. One common type of OAE is distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) generated by the cochlea when the ear is stimulated with two simultaneous tones (termed primary tones, or primaries) at levels L1 and L2 (the primary levels) at frequencies f1 and f2 (the primary frequencies), correspondingly. The most prominent (and clinically evaluated) distortion product occurs at 2f1-f2, and is termed the cubic difference tone [2,3].
Acoustic stimulation of the opposite ear induces changes in DPOAE levels (usually reductions) in both animals and humans [4,5]. This phenomenon is commonly termed contralateral suppression (CS). DPOAE CS is likely attributable to suppression of cochlear mechanical responses by activation of the medial olivocochlear (MOC) efferents by acoustic stimulation [6,7]. Thus, suppression of DPOAE by contralateral acoustic stimulation (CAS) is often used to explore suppression mediated by the contralateral MOC reflex and to assess the functional integrity of the MOC efferent system [8,9].
The clinical applications of DPOAE CS measurements are limited; the CS is relatively low in humans (1-2 dB). Any L2 effect on DPOAE CS has not been comprehensively studied. Wagner, et al. [10] claimed that the primary levels critically influenced the amount of DPOAE CS. However, the cited authors used only five frequencies (f2=2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 Hz) when seeking to define the optimal primary level that should be used to evoke DPOAE CS [11]. Another study claimed that maximum suppression and enhancement were evident principally in the low L2 region (30 dB) [12]. However, no statistical data were presented and primary levels (e.g., L1 and L2) >60 dB were not investigated.
It is commonly accepted that two mechanisms contribute to DPOAE generation: nonlinear distortion and coherent reflection [13,14]. Emission from the overlap region of f2 (the distortion source) and from the 2f1-f2 region (the reflection source) mix on the way to the ear canal. Their vector sum is the final DPOAE. Interaction between the two DPOAE components produces a pattern of alternating maxima (peaks) and minima (dips) known as the DPOAE fine structure. The amount of CS is known to vary through the peaks and dips; suppression is generally evident at the fine structure peaks of DPOAE, with enhancement or lower-level suppression apparent at the dips [15-17]. It is important to measure DPOAE-mediated CS at multiple frequencies to allow for DPOAE variability throughout the fine structure.
In this study, we measured changes in DPOAE levels caused by contralateral broadband noise (BBN) delivered between 1,000 Hz and 6,727 Hz at 8 pt/octave, at various primary L2 levels. We thus evaluated the effects of primary levels and frequencies on DPOAE-mediated CS.
Sixteen subjects (total 32 ears) participated (10 males; age, 25.44┬▒4.62 years). All subjects underwent tympanometry, ipsilateral and contralateral acoustic stapedial reflex testing, and pure tone audiometry. All subjects had normal pure tone hearing thresholds (Ōēż15 dB hearing level) at all octave intervals from 250 to 8,000 Hz. All subjects had ŌĆ£AŌĆØ type tympanograms, exhibited no stapedial reflex at Ōēż80 dB, and had no history of ear disease or a neurological disorder. All subjects gave written informed consent prior to participation. The Institutional Review Board of Kangwon National University Hospital reviewed and approved the study protocol (KNUH-2011-01-001).
A MADSEN Astera audiometer running OTOsuite software (GN Otometrics, Taastrup, Denmark) was used to obtain tympanograms and measure pure tone thresholds. DPOAEs were obtained using an ILO V6 clinical OAE system (Otodynamics Ltd., Hatfield, UK) as described below. All subjects silently read newspapers during measurements to ensure that they were awake and conscious.
All measurements were obtained in a double-walled soundproof room (ISO 8253-1). The 2f1-f2 DPOAE was measured for f2 frequencies between 841 Hz and 8,000 Hz, with 8 pt/octave (total, 27 frequencies), in both ears of all subjects. DPOAE was measured using a standard adult ear probe with a foam eartip; the probe was inserted into the ear canal. Stimuli were presented through calibrated headphones (TDH39; GN Otometrics) with a primary frequency ratio (f2/f1) of 1.22. The primary levels varied as follows: L1=0.4L2+39; L2=40, 50, 60, 70, and 80 dB SPL.
The DPOAE was first recorded without CAS, and then recorded again with continuous BBN presented contralaterally through one of the headphones at 65 dB SPL. Both measurements were repeated for each pair of primary levels. The order of recordings (different primary levels, and with/without CAS) was counterbalanced among subjects. The level of 65 dB was chosen for the contralateral BBN in this study as a level sufficiently high to produce ample DPOAE CS, yet unlikely to trigger the stapedial reflex [18,19]. Twenty DPgrams (under five no-CAS conditions and five CAS conditions, ten conditions per ear) were obtained from each subject during a single session, which lasted about 10 min.
The amount of DPOAE CS (or simply DPOAE CS) was calculated by subtracting CAS-suppressed DPOAE from the baseline DPOAE level. A positive value indicated DPOAE suppression, and a negative value enhancement. All statistical analyses were performed with the aid of SPSS software (version 21.0; IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
In linear-mixed model analysis, we used only individual DPOAE values Ōēź6 dB above the noise floor. Values with signal-to-noise ratios <6 dB and outliers were removed. Outliers were defined as values with z-scores >3.29 or <-3.29. Data obtained at the two lowest (841 Hz and 917 Hz) and the two highest (7,336 Hz and 8,000 Hz) frequencies were excluded from analysis because we lacked an adequate number of data points. Thus, the final analyses were of data obtained at 23 frequencies (range, 1,000-6,727 Hz).
We used a linear mixed model (LMM) to evaluate the DPOAE CS dataset, using the MIXED procedure of SPSS, which allows LMMs to be fitted to sampled data. An LMM is more general than a general linear model (GLM) and was preferred for several reasons. First, an LMM extends the repeated measures capacities of GLMs to accommodate unequal numbers of repetitions, as in the present study. GLMs eliminate the entire case if even one data point is missing, whereas LMMs use all remaining data. Second, unlike a GLM, an LMM allows straightforward post-hoc testing of within-subject factors. Finally, unlike a GLM, an LMM does not assume sphericity, which is often in fact absent.
The LMM fixed factors included the side of the ear, gender, f2, L2, and interaction terms f2 and L2. The latter term was included to explore if the L2 effect depended on the frequency. We did not include age; all subjects were of similar age. We employed the maximum likelihood method with a first-order autoregressive covariance structure AR(1). This structure exhibits homogeneous variances and correlations that decline exponentially with distance. This meant that, with our data, any variability in measurement was constant regardless of when the measurement was taken. We used the Bonferroni adjustment for post-hoc comparisons to control for type I errors; the level of significance was set at 0.05.
A paired t-test was used to compare the baseline and suppressed DPOAE datasets (concatenated through L2 and f2) for each frequency, to identify frequencies associated with significant suppression.
The depth of DPOAE fine structure was evaluated using the discrete cosine transform (DCT) method [20], which requires that all data series must have the same length. Thus, our data inclusion criterion was based on the median signalto-noise ratio (SNR) calculated as the difference between the median DPOAE level (dB SPL) across the entire frequency range and the median noise level (dB SPL) over the same range. Only ears with SNRs >9 dB were included in analysis. The DCT method was used to evaluate log-magnitude baseline (no CAS) DPOAE and suppressed (with CAS) DPOAE data after averaging information from all subjects across the entire frequency range; we calculated the levels of various components of the DPOAE response. The DC component, thus varying at 0 cycles/octave, can be viewed as representing the overall level of the response. The high- frequency components of the DCT represent fluctuations in the DPOAE response around the overall level and can be used to evaluate the fine structure [21,22]. The root mean square (RMS) of the DCT high-frequency components was calculated as a single measure of fine structure depth. The DCT RMSs were further compared across the primary levels of the baseline and suppressed DPOAE data using repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons (p<0.05).
Tables 1 and 2 show the results of the LMM and estimates of the fixed effects (e.g., the estimated fixed factors associated with ear, gender, f2, and L2) for DPOAE CS, respectively. The effects of both frequency and gender were significant (p<0.001 for both). No significant effect was evident in terms of primary level, ear side, or the interaction between primary level and frequency. Fig. 1A shows the DPOAE CSs for each primary level plotted as a function of f2. Fig. 1B shows the mean DPOAE CSs across L2.
Females exhibited more DPOAE CS than males (means, 1.49┬▒0.15 dB SPL and 0.46┬▒0.12 dB SPL, respectively). Fig. 2A, B shows the DPOAE CSs for each f2 as a function of L2 and the mean DPOAE CSs across f2, respectively. The DPOAE CS exhibited a wave-like distribution pattern with f2; f2 values of 1,091 Hz and 1,297 Hz (on the left of the measured frequency range) produced significantly greater CSs than f2 values of 2,000-3,364 Hz. An f2 value of 1,189 Hz afforded a higher CS than f2 values of 2,000, 2,378, or 2,594 Hz. The primary frequencies f2 of 5,657 Hz and 6,727 Hz produced higher DPOAE CSs than 2,000 Hz and 2,594 Hz.
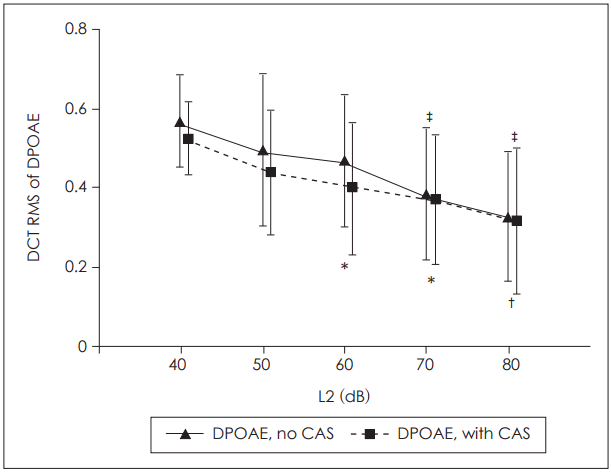
Suppression was significant for all L2 values when the DPOAE values were concatenated through the primary frevalquencies (p<0.05 after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons) (Fig. 3A). When concatenated through the primary levels, f2 values of 1,000-1,297 Hz and 5,187-6,727 Hz exhibited significant DPOAE suppression (Fig. 3B).
In this portion of the study, we excluded two subjects (four ears) from analysis using the abovementioned exclusion criteria. Thus, we used the DCT method to evaluate 28 ears.
We found that the effect of primary level on the DCT RMS was significant for both the baseline and contralaterally stimulated DPOAEs (p<0.001 for both datasets; repeated measures ANOVA). Fig. 4 shows the mean DCT RMS values and the results of pairwise comparisons (p<0.05; Bonferroni-corrected). In the baseline DPOAE dataset, the DCT RMSs at L2=70 dB and 80 dB were significantly lower than those at L2=40, 50, and 60 dB. In the contralaterally stimulated DPOAE dataset, the DCT RMS at L2=80 dB was significantly lower than those at L2=40 dB and 50 dB. At L2=60 dB and 70 dB, the DCT RMSs were significantly lower than that at L2=40 dB. Thus, the DPOAE fine structure depth fell significantly as stimulus intensity increased, with or without contralateral stimulation.
Two earlier studies exploring the effects of primary level on DPOAE CS found that the CS was greater at low L2 levels (30-40 dB) [11,12]. However, in both studies, L2 was varied only from 20 to 60 dB SPL; the two highest L2 levels (70 dB and 80 dB) were not explored. Furthermore, no statistical comparison of DPOAE CS across the primary levels was performed in either study; the authors described only the trend (CS decreased with an increase in L2). The same trend (a decrease in CS as L2 increased from 40 dB to 60 dB) is evident in our present study (Fig. 1B). However, at the higher two stimulus levels (70 dB and 80 dB), CS increased once more (0.91┬▒4.95 dB vs. 0.43┬▒4.24 dB vs. 0.77┬▒4.12 dB at L2=40, 60, and 80 dB, respectively). As CS first decreased and then increased as L2 increased, we analyzed two datasets containing only the three lowest and the three highest L2 values to determine if separate L2 effects were apparent for each trend. L2 was not statistically significant in either dataset (data not shown). As the cited studies did not claim that statistical significance was apparent, the suggestion that CS is greater at lower L2 levels is debatable.
The interaction between primary level (L2) and the primary stimulus frequency (f2) was not significant. However, we found that the effect of frequency was in fact significant (Table 1). Several studies found that most CAS effects were evident at 1-2 kHz [4,23,24]. However, other studies did not support this contention; DPOAE CS varied in different ways depending on the primary frequency [16,25,26]. In our study, the extremes of frequency bands centered at f2=1,189 Hz and 5,657 Hz afforded significantly greater DPOAE CS than did the mid-range stimulus frequencies (2 kHz to 4 kHz) (Fig. 2B). The results of the paired t-test were in line with this observation, showing that the first and last four explored frequencies were associated with significant differences between baseline and suppressed DPOAE values when they were concatenated through L2 (Fig. 3B). Thus, DPOAE CS was highly dependent on primary frequency, emphasizing the importance of measuring DPOAE CS over a wide range of frequencies (rather than just a few audiometric frequencies, as is usually the case in clinical settings). In addition, the frequencies that produced the greatest baseline DPOAE also resulted in the highest CS (Fig. 2B, 3B), suggesting that baseline DPOAE measurements may be used to make a priori choices of the best frequency or frequency band to use when measuring a CAS effect.
We additionally analyzed the effect of L2 on DPOAE fine structure depth because no direct effect of the primary level on DPOAE CS was evident. DPOAE fine structure is believed to arise from constructive and destructive interactions between the two sources. When the distortion and reflection components of DPOAE are in phase, a peak in fine structure is evident. If the two components combine while out of phase, a dip results [3]. It has been speculated that CAS influences the two DPOAE components differently, suppressing one component more than the other, thus either suppressing or enhancing the overall DPOAE level [27]. In other words, when the two components are in phase, thus summing constructively to create a fine structure peak, a reduction in the amplitude of one or both components mediated by CAS will lower their total sum (the final DPOAE). In contrast, when the components sum destructively out of phase, CAS suppression of only one component will weaken the mutual cancellation, increasing (enhancing) the final DPOAE. It has been suggested that DPOAE CS should be measured at fine structure dips, which seem to be associated with maximal MOC reflex effects [10,12]. Therefore, the importance of DPOAE fine structure should not be underestimated. The frequency step (1/8 octave) used in our study may not be adequate to evaluate fine structure in detail; the peak-to-peak frequency spacing is approximately 3/32 octave [28]. However, our frequency resolution was considerably higher than that used in regular DPOAE clinical protocols, and most studies in the literature.
As the fine structure is the outcome of an unknown mixture of more than one contributory component, this may impose limitations on the use of DPOAEs to predict cochlear function. Furthermore, if the DPOAE response minimum falls to the frequency at which cochlear function is being tested, a normal ear can be misdiagnosed as impaired, and vice versa. Additionally, DPOAE level variation yields normative data associated with a large range of variance. This means that the response distributions overlap between normal and hearing-impaired subjects, limiting the potential of correlational analyses to consistently predict hearing thresholds [29].
It has therefore been suggested that a choice of stimulus parameters minimizing fine structure depth could improve the clinical applications of DPOAE [22,30]. In our present study, the fine structure depth fell consistently as the L2 level increased, both for baseline and suppressed DPOAE (Fig. 4). This created significant differences between lower and higher L2 levels, suggesting that use of higher primary levels would reduce variation in DPOAE levels and improve clinical applicability.
It should be noted, however, that high-level stimuli (for example, those around 80 dB) may trigger a passive cochlear contribution to the measured outcomes. In addition, such highlevel stimuli can evoke ipsilateral effects causing DPOAE adaptations, creating situations caused by a mixture of contralateral and ipsilateral stimulation. Further studies are needed to explore the mechanism of DPOAE evoked by high-level stimuli in greater detail.
In conclusion, low and high frequencies were associated with more DPOAE CS than were middle-level frequencies. The frequencies associated with the greatest baseline DPOAE also afforded the greatest suppression. Higher L2 levels appeared to significantly reduce the DPOAE fine structure depth, although the primary level did not seem to affect DPOAE CS. Our results suggest that use of a higher L2 level (60-80 dB SPL) could produce high-level DPOAE CS with simultaneous reduction of the DPOAE fine structure. Although higher primary levels have not received much attention, and require further investigation, we have taken a step toward improving the clinical procedures used to evaluate MOC reflex and to assess the function of the auditory efferent system.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a 2015 Research Grant from Kangwon National University (No. 520150335).
Fig.┬Ā1.
Mean DPOAE CSs produced by different L2 levels (A) and different f2 frequencies (B). The DPOAE CS was averaged over all ears. DPOAE: distortion product otoacoustic emission, CS: contralateral suppression.

Fig.┬Ā2.
Mean DPOAE CSs averaged over primary frequencies f2 (A) and primary levels L2 (B). No significant influence of primary level was evident. The primary frequency effect was significant, with lateral frequencies exhibiting significantly higher suppression than midfrequencies within the explored frequency range. DPOAE: distortion product otoacoustic emission, CS: contralateral suppression.
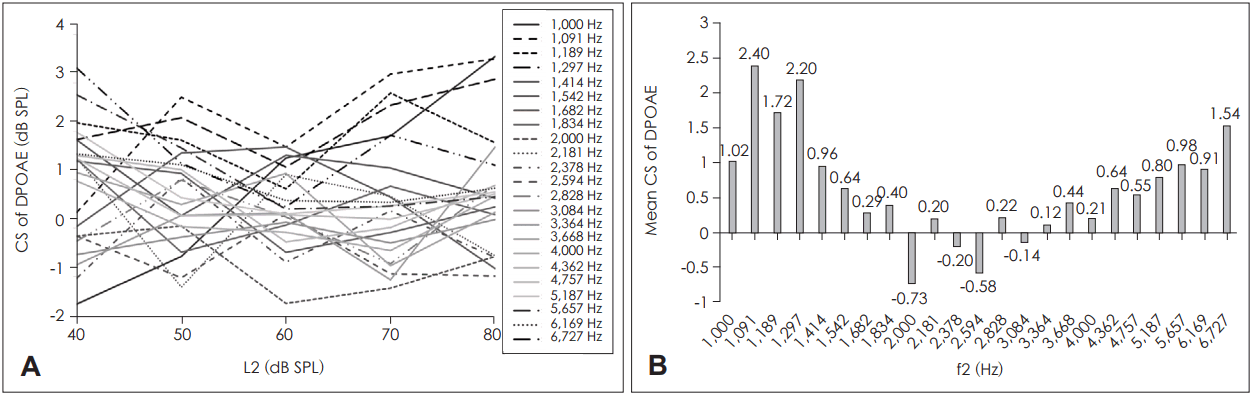
Fig.┬Ā3.
Results of paired t-testing of DPOAE with and without CAS. A: When averaged over the primary frequencies, suppression was significant for all L2. B: When averaged over the primary levels, suppression was significant for the first four and the last four frequencies of the studied f2 range. *significant at p<0.05; paired t-test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. DPOAE: distortion product otoacoustic emission, CAS: contralateral acoustic stimulation.
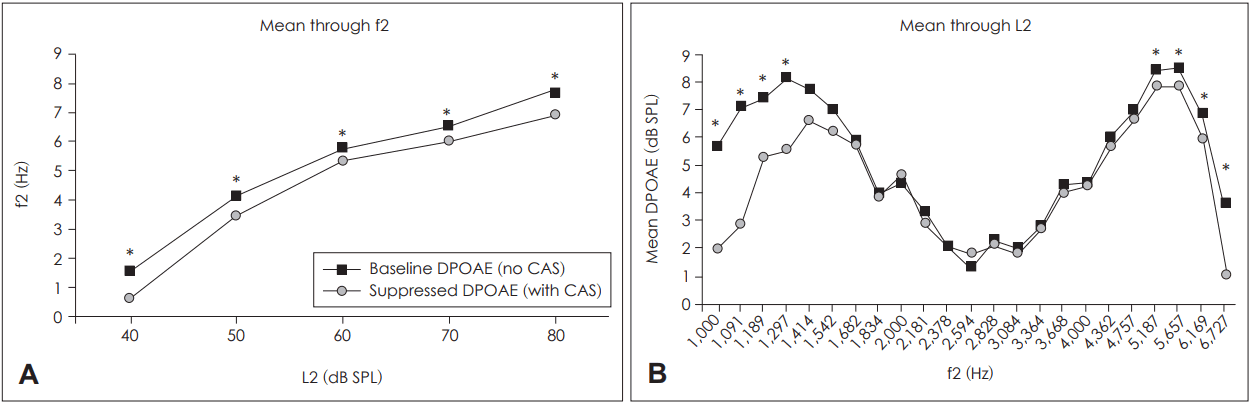
Fig.┬Ā4.
Depth of the fine structure of the baseline and suppressed DPOAE datasets as revealed by the DCT RMS values. Mean DCT RMSs averaged over ears and primary frequencies are plotted as functions of L2. The error bars represent┬▒one standard deviation of the mean. *difference compared to L=40 dB, ŌĆĀdifference compared to L=40 dB and 50 dB, ŌĆĪdifference compared to L=40, 50, and 60 dB; statistically significant at p<0.05, paired t-test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons. DPOAE: distortion product otoacoustic emission, DCT: discrete cosine transform, RMS: root mean square.
Table┬Ā1.
Linear mixed model maximum-likelihood estimates of fixed effects with various primary levels (dependent variable: distortion product otoacoustic emission contralateral suppression)
| Source | Numerator df | Denominator df | F-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ear side | 1 | 643.11 | 53.54 | 0.427 |
| Gender | 1 | 647.79 | 0.63 | <0.001* |
| L2 | 4 | 697.32 | 0.64 | 0.635 |
| f2 | 22 | 1,689.75 | 3.57 | <0.001* |
| L2*f2 | 88 | 1,697.28 | 1.20 | 0.107 |
Table┬Ā2.
Linear mixed model maximum-likelihood estimates of fixed effects with various primary levels (dependent variable: distortion product otoacoustic emission contralateral suppression)
| Parameter | Estimate | SE | T | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender=M | -1.443 | 0.197 | -7.317 | <0.001* |
| Gender=FŌĆĀ | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
| Ear=R | 0.152 | 0.192 | 0.794 | 0.427 |
| Ear=LŌĆĀ | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
| L2=40 | 1.733 | 1.211 | 1.430 | 0.153 |
| L2=50 | 0.146 | 1.089 | 0.134 | 0.893 |
| L2=60 | -0.788 | 1.079 | -0.730 | 0.465 |
| L2=70 | 0.611 | 1.054 | 0.580 | 0.562 |
| L2=80ŌĆĀ | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
| f2=1,000 | 2.542 | 1.142 | 2.226 | 0.026* |
| f2=1,091 | 2.157 | 1.071 | 2.013 | 0.044* |
| f2=1,189 | 0.257 | 1.071 | 0.240 | 0.811 |
| f2=1,297 | 1.670 | 1.062 | 1.572 | 0.116 |
| f2=1,414 | -0.654 | 1.047 | -0.625 | 0.532 |
| f2=1,542 | -1.977 | 1.070 | -1.847 | 0.065 |
| f2=1,682 | -1.004 | 1.079 | -0.930 | 0.352 |
| f2=1,834 | -1.070 | 1.070 | -1.000 | 0.318 |
| f2=2,000 | -1.977 | 1.070 | -1.848 | 0.065 |
| f2=2,181 | -1.839 | 1.047 | -1.756 | 0.079 |
| f2=2,378 | -2.006 | 1.054 | -1.903 | 0.057 |
| f2=2,594 | -2.340 | 1.078 | -2.170 | 0.030* |
| f2=2,828 | -0.560 | 1.097 | -0.511 | 0.610 |
| f2=3,084 | -1.091 | 1.080 | -1.010 | 0.312 |
| f2=3,364 | 0.236 | 1.080 | 0.219 | 0.827 |
| f2=3,668 | -0.993 | 1.064 | -0.934 | 0.350 |
| f2=4,000 | -0.670 | 1.063 | -0.630 | 0.529 |
| f2=4,362 | -0.405 | 1.054 | -0.384 | 0.701 |
| f2=4,757 | -0.582 | 1.058 | -0.550 | 0.582 |
| f2=5,187 | -0.526 | 1.035 | -0.508 | 0.611 |
| f2=5,657 | -0.623 | 1.004 | -0.620 | 0.535 |
| f2=6,169 | -0.448 | 0.889 | -0.504 | 0.614 |
| f2=6,727ŌĆĀ | 0.000 | 0.000 | - | - |
REFERENCES
1. Kemp DT. Stimulated acoustic emissions from within the human auditory system. J Acoust Soc Am 1978;64:1386ŌĆō91.


2. Mauermann M, Uppenkamp S, van Hengel PW, Kollmeier B. Evidence for the distortion product frequency place as a source of distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) fine structure in humans. I. Fine structure and higher-order DPOAE as a function of the frequency ratio f2/f1. J Acoust Soc Am 1999;106:3473ŌĆō83.


3. Dhar S, Long GR, Talmadge CL, Tubis A. The effect of stimulusfrequency ratio on distortion product otoacoustic emission components. J Acoust Soc Am 2005;117:3766ŌĆō76.


4. Moulin A, Collet L, Duclaux R. Contralateral auditory stimulation alters acoustic distortion products in humans. Hear Res 1993;65:193ŌĆō210.


5. Liberman MC, Puria S, Guinan JJ Jr. The ipsilaterally evoked olivocochlear reflex causes rapid adaptation of the 2f1-f2 distortion product otoacoustic emission. J Acoust Soc Am 1996;99:3572ŌĆō84.


6. Guinan JJ Jr. Olivocochlear efferents: anatomy, physiology, function, and the measurement of efferent effects in humans. Ear Hear 2006;27:589ŌĆō607.


7. Guinan JJ Jr. Cochlear efferent innervation and function. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;18:447ŌĆō53.



8. James AL. The assessment of olivocochlear function in neonates with real-time distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Laryngoscope 2011;121:202ŌĆō13.


9. Di Girolamo S, Napolitano B, Alessandrini M, Bruno E. Experimental and clinical aspects of the efferent auditory system. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2007;97(Pt 2):419ŌĆō24.

10. Wagner W, Heppelmann G, M├╝ller J, Janssen T, Zenner HP. Olivocochlear reflex effect on human distortion product otoacoustic emissions is largest at frequencies with distinct fine structure dips. Hear Res 2007;223:83ŌĆō92.


11. Wagner W, Heppelmann G, Kuehn M, Tisch M, Vonthein R, Zenner HP. Olivocochlear activity and temporary threshold shift-susceptibility in humans. Laryngoscope 2005;115:2021ŌĆō8.


12. M├╝ller J, Janssen T, Heppelmann G, Wagner W. Evidence for a bipolar change in distortion product otoacoustic emissions during contralateral acoustic stimulation in humans. J Acoust Soc Am 2005;118:3747ŌĆō56.


13. Mauermann M, Kollmeier B. Distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) input/output functions and the influence of the second DPOAE source. J Acoust Soc Am 2004;116(4 Pt 1):2199ŌĆō212.


14. Talmadge CL, Long GR, Tubis A, Dhar S. Experimental confirmation of the two-source interference model for the fine structure of distortion product otoacoustic emissions. J Acoust Soc Am 1999;105:275ŌĆō92.


15. Williams DM, Brown AM. The effect of contralateral broad-band noise on acoustic distortion products from the human ear. Hear Res 1997;104:127ŌĆō46.


16. Henin S, Thompson S, Abdelrazeq S, Long GR. Changes in amplitude and phase of distortion-product otoacoustic emission fine-structure and separated components during efferent activation. J Acoust Soc Am 2011;129:2068ŌĆō79.


17. Zhang F, Boettcher FA, Sun XM. Contralateral suppression of distortion product otoacoustic emissions: effect of the primary frequency in Dpgrams. Int J Audiol 2007;46:187ŌĆō95.


18. Gelfand SA. The contralateral acoustic-reflex threshold. In: Silman S. editor. The acoustic reflex. Orlando, FL: Academic Press;1984. p.137ŌĆō86.
19. Margolis RH. Detection of hearing impairment with the acoustic stapedius reflex. Ear Hear 1993;14:3ŌĆō10.


20. Rao KR, Yip P. Discrete cosine transform: algorithms, advantages, applications. San Diego, CA: Academic Press;1990.
21. Johnson TA, Neely ST, Kopun JG, Dierking DM, Tan H, Converse C, et al. Distortion product otoacoustic emissions: cochlear-source contributions and clinical test performance. J Acoust Soc Am 2007;122:3539ŌĆō53.



22. Johnson TA, Baranowski LG. The influence of common stimulus parameters on distortion product otoacoustic emission fine structure. Ear Hear 2012;33:239ŌĆō49.


23. Lisowska G, Smurzynski J, Morawski K, Namyslowski G, Probst R. Influence of contralateral stimulation by two-tone complexes, narrow-band and broad-band noise signals on the 2f1-f2 distortion product otoacoustic emission levels in humans. Acta Otolaryngol 2002;122:613ŌĆō9.


24. Atcherson SR, Martin MJ, Lintvedt R. Contralateral noise has possible asymmetric frequency-sensitive effect on the 2F1-F2 otoacoustic emission in humans. Neurosci Lett 2008;438:107ŌĆō10.


25. Ozimek E, Wicher A. Changes in distortion product otoacoustic emission caused by contralateral broadband noise. Archi Acoust 2014;39:125ŌĆō38.

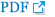
26. Lisowska G, Namyslowski G, Orecka B, Misiolek M. Influence of aging on medial olivocochlear system function. Clin Interv Aging 2014;9:901ŌĆō14.



27. Abdala C, Mishra SK, Williams TL. Considering distortion product otoacoustic emission fine structure in measurements of the medial olivocochlear reflex. J Acoust Soc Am 2009;125:1584ŌĆō94.



28. He NJ, Schmiedt RA. Fine structure of the 2f1-f2 acoustic distortion product: changes with primary level. J Acoust Soc Am 1993;94:2659ŌĆō69.