 |
 |
- Search
| J Audiol Otol > Volume 22(3); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Background and Objectives
To prevent noise induced hearing losses caused by listening to music with personal listening devices for young adults, this study was aimed to measure output levels of an MP3 and to identify preferred listening levels (PLLs) depending on earphone types, music genres, and listening durations.
Subjects and Methods
Twenty-two normal hearing young adults (mean=18.82, standard deviation=0.57) participated. Each participant was asked to select his or her most PLLs when listened to Korean ballade or dance music with an earbud or an over-the-ear earphone for 30 or 60 minutes. One side of earphone was connected to the participantŌĆÖs better ear and the other side was connected to a sound level meter via a 2 or 6 cc-couplers. Depending on earphone types, music genres, and listening durations, loudness A-weighted equivalent (LAeq) and loudness maximum time-weighted with A-frequency sound levels in dBA were measured.
Results
Neither main nor interaction effects of the PLLs among the three factors were significant. Overall output levels of earbuds were about 10-12 dBA greater than those of over-the-ear earphones. The PLLs were 1.73 dBA greater for earbuds than over-the-ear earphones. The average PLL for ballad was higher than for dance music. The PLLs at LAeq for both music genres were the greatest at 0.5 kHz followed by 1, 0.25, 2, 4, 0.125, 8 kHz in the order.
Conclusions
The PLLs were not different significantly when listening to Korean ballad or dance music as functions of earphone types, music genres, and listening durations. However, over-the-ear earphones seemed to be more suitable to prevent noise induce hearing loss when listening to music, showing lower PLLs, possibly due to isolation from the background noise by covering ears.
Development in technology of modern science has inevitably brought upon harmful noise to peopleŌĆÖs health in exchange for enriching their lives. Consequently, the noise may cause permanent hearing loss which could lead to stress, annoyance, depression and limited communication. However, in the early stage of hearing loss, people may not experience any difficulty in everyday conversational situations. Therefore, the accumulated hazard accounting for hearing loss by listening to music during leisure activities have been described in the literature across the nations [1-5].
Personal listening devices (PLDs), such as MP3 players, portable multimedia player, smartphones etc., continued to develop increasing data storage for storing up to 40,000 songs with longer battery life for up to 30-40 hours [6]. The extended amount of hours of use for the variety of the PLDs resulted in a higher risk of noise induced hearing loss for listening to music. According to Portnuff, et al. [7], improper use of PLDs caused hearing loss by two potential elements including individualŌĆÖs preferred listening levels (PLLs) and exposure duration. The background noise seemed to be one of the factors affecting PLLs, because the PLL increased as the background noise level increased [8]. Reducing the background noise was also proposed as one of the resolving methods [9,10]. Also, the effects of earphone type and music genre had been reported differing views among researchers as the factors affecting PLLs [4,7,11].
Concerning the earphone types, it was known that the smaller types of earphone produced the greater output levels due to the location to near the tympanic membrane. When the maximum output levels were measured in the different types of earphones of MP3 players, earbuds reported 100.8 dBA and in-the-ear earphones reported at 102.3 dBA, and over-the-ear earphones reported 96.7 dBA [7]. Although one study showed the highest PLLs at over-the-ear earphones in quiet and noisy environments out of three types of earphones [8], PLLs were measured significantly lower when using over-the-ear earphones than the other two earphones in many studies [10,12,13].
Researches investigating the music genre have produced mixed results about maximum output levels. Previous studies indicated that the highest maximum output levels of rock or pop music among several music genres such as rock, hip-hop, and ballade [4,9]. And when the maximum output levels were measured at 10 music styles arbitrarily classifying into three groups depending on the sound level, low with the classical music style, medium with folk, pop, salsa/Latin, classic rock, and Latin-pop music styles, and high with electronic, heavy/metal, reggaeton, and hip-hop music styles, the groups showed the significant difference with 14.4 dB difference [10]. But, the other study reported that there was no significant difference in output levels according to music genres among rock, R&B, country, and dance with the maximum volume setting [14]. Additionally, one study reported about PLLs depending on music genres indicating significant difference between two music genres, electronica and hip-hop with 24 college students [15].
In order to determine the hazardous sound levels of music, standards for occupational noise exposure be adopted for calculating and managing music induced hearing loss. The International Standard Organization (ISO) and National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) made standard and defined regulations for occupational noise. That is a time-weighted average (TWA) level at 85 dBA for an 8 hour period per day as the maximum permissible dose of sound energy [16,17]. In Korea, Korean Occupational Safety Health Agency (KOSHA) has proposed a TWA level at 90 dBA for an 8 hour period per day as the maximum permissible exposure.
In study of PLD usage and knowledge of 180 college students using self-reports, length of listening time to be harmful to hearing was perceived as 30 minutes for 11% of the student, 60 minutes for 34%, 120 minutes for 36%, and 180 minutes for 19 % indicating the importance of listening duration [2]. Considering the results, there was the perception change between the listening durations of 30 and 60 minutes. For college students, it was found to be at risk due to listening to music with PLDs in excess of safe listening levels and durations [13], the listening time for music draw particular interests with music genres and earphone types to determine healthy listening habits for young adults.
For providing basic information to build up the good listening habits and preventing noise induced hearing losses caused by listening to music with PLDs for young adults, it is necessary to investigate all the factors which affect the output levels and PLLs of PLDs. Therefore, this study was aimed to measure output levels of an MP3 player according to the volume levels and to identify PLLs depending on earphone types, music genres, and listening durations.
Twenty-two young adults (11 males, 11 females) with normal hearing participated after signing consent forms. Their age ranged from 18 to 20 years of age (mean=18.82, standard deviation=0.57). The hearing thresholds were at 15 dB HL or better in the frequency range of 0.25 to 8 kHz and type A tympanograms bilaterally were assessed for all the participants. None of the participants had any etiological factors of the ear pathology and were exposed to noise and/or music for at least 24 to 48 hours prior to the experiment. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hallym University (HIRB-2014-90).
Two types of earphones, earbuds and over-the-ear earphones, were utilized for this experiment. Those were LMXE112 earbuds (Cresyn, Seoul, Korea) and BKS-40 over-the-ear earphones (Actto, Busan, Korea). The frequency range of the earphones was 20-20,000 Hz. The impedances of the earphones were 16 ╬® and 32 ╬®, respectively. LPlayer (Iriver, Seoul, Korea) MP3 player that had volume levels ranging from #0, representing no sound to #40, representing maximum volume were used. It was fully charged before being turned on.
The sound level meter type 2250 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r, N├”rum, Denmark) was used. The microphones were prepolarized free field 1/2ŌĆ│ microphone type 4189 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r) for measuring background noise levels and pressure-field 1/2ŌĆ│ microphone type 4192 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r) for measuring output levels of the earphones. The calibration was performed by a sound calibrator type 4231 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r). The measurement parameters were loudness A-weighted equivalent (LAeq) and loudness maximum time-weighted A-frequency (LAFmax). LAeq is a widely used noise parameter that calculates an average constant level of sound when the fluctuating acoustic signals are measured. LAFmax is the highest level of sound occurring during the whole measurement time. The other parameters were fast time weighting, 1/1 octave bandwidth, automatic measurement control and free-field sound field correction. Measurement partner suite BZ-5503, an analysis program linked with PC software, presented from Br├╝el & Kj├”r, was to analyze the measured sound levels. The output levels generated by the MP3 player were estimated at eight-hour equivalent continuous loudness with LAeq.8h which was calculated and analyzed in this experiment using the same formula provided by many researchers [5,11,18-20]. In these previous studies, LAeq┬Ę8h was defined as ŌĆśa steady state sound pressure level which would in the course of an eight hour period deliver the same A-weighted sound energy on any particular representative working dayŌĆÖ and mathematically calculated from the equation below.
The music genre used for this experiment was drawn randomly from a pool of Korean 7 ballad and 9 dance songs selected from the popular music chart of Melon(www.melon.com) which was online music service site. The transmitting speed was 320 kilobits per second bit rate and the sampling rate was 44.1 kHz. For 30 minutes of duration, the music was edited by Goldwave ver. 5.88 (Goldwave, Saint JohnŌĆÖs, Canada) for equalizing the maximum volume and channel of each song. For 60 minutes of duration, the edited 30 minutes duration of music was played repeatedly. Two listening durations, 30 and 60 minutes, were applied.
One side of earphone was connected to the participantŌĆÖs better ear and the other side was connected to the sound level meter to measure output levels. The earbud and over-the-ear earphones were attached to the plug socket located top of the sound level meter using preamplifier ZC 0032 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r) with 2 cc click-on coupler type 4946 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r) and with 6 cc coupler artificial ear stimulator type 4153 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r) connected to extensions cable AO 0441 (Br├╝el & Kj├”r). The music was randomly played to avoid any learning effect. The MP3 screen was covered in order for preventing any bias for selecting PLLs.
The experiment was carried out in a quiet room at Hallym Speech and Hearing Center while keeping the environmental noise quiet enough to perform the experiment. The average ambient noise in the room was 24.7 dBA ranging from 17.9 dBA to 29.2 dBA , which was designed to be under the provision of ANSI S3.1 (1999) [21] and OSHA [22]. Specifically, the ambient noise levels were maintained at 13.6 dBA for 0.125 kHz, at 17.4 dBA for 0.25 kHz, at 18.1 dBA for 0.5 kHz, at 16.0 dBA for 1 kHz, at 14.0 dBA for 2 kHz, at 17.0 dBA for 4 kHz, at 11.3 dBA for 8 kHz.
The data were statistically analyzed using a repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) with SPSS ver. 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Three independent variables, 2 earphone types, earbuds and over-the-ear earphones, 2 music genres, ballad and dance, and 2 listening durations, 30 and 60 minutes were analyzed by the dependent variables, output levels, in LAeq and LAFmax. p value of <0.05 was considered significant.
Output levels were measured on various volume levels of the MP3 player. The LAeq and LAFmax for 30 minutes at volume #10 (25%), #20 (50%), #30 (75%), and #40 (100%) indicated increasing intensity as the volume setting number increased for both music genres in both earphone types. When listening to ballad, the range of LAeq was 70.9-115.5 dBA for earbuds and 57.3-104.3 dBA for over-the-ear earphones indicating 12.55 dBA higher for the earbuds in average. When listening to dance, the range of LAeq was 73.4-117.9 dBA for earbuds and 60.7-107.5 dBA for over-the-ear earphones indicating 10.73 dBA higher for the earbuds in average. LAFmax showed higher levels in earbuds, as well (Table 1). 60 minutes duration was not provided because they were identical to 30 minutes of duration as they played repeatedly.
When the volume settings were selected for the PLLs, out of #0~#40, the mean volume settings of the MP3 player were higher for the over-the-ear earphone at #14 and #10 over #7 and #6 out of two earphone types and in ballade music at #7 and #14 over #6 and #10 out of two music genres. However, LAeq were the higher a little for the earbud than over-the-ear earphones and LAFmax was almost the same regardless of earphone types and music genres except the combination of the over-the-ear earphone with dance music. Therefore, for both LAeq and LAFmax, the PLLs were the lowest for the combination of the over-the-ear earphone with dance music reporting 63.4 and 74.8 dBA (Table 2).
When the average PLLs according to the three variables were compared, over-the-earphones, ballade, and 30minutes of duration showed higher output levels (Table 3). However, repeated-measures ANOVA indicated all three main and interaction effects were not significant.
LAeq was converted to eight-hour equivalent continuous loudness depending on the formula and compared to the criteria of the KOSHA and NIOSH, the PLLs were measured from 50 to 55 dBA for earbuds and from 45 to 60 dBA for over-the-ear earphones, showing a wider range for over-theear earphones. When they listened to ballade music for 30 minutes with earbud and over-the-ear earphones, LAeq┬Ę8hŌĆÖs were 48.87-85.87 dBA (mean=57.97, standard deviation=8.43) and 43.17-98.77 dBA (mean=57.46, standard deviation=11.90). When they listened to dance music for 30 minutes with earbud and over-the-ear earphones, LAeq┬Ę8hŌĆÖs were 56.97-86.47 dBA (mean=58.00, standard deviation=8.18) and 41.07-84.17 dBA (mean=54.47, standard deviation=10.19). When they listened to ballade music for 60 minutes with earbud and over-the-ear earphones, LAeq┬Ę8hŌĆÖs were 48.87-89.27 dBA (mean=57.10, standard deviation=9.54) and 31.47-89.67 dBA (mean=56.14, standard deviation=12.35). When they listened to dance music for 60 minutes with earbud and over-the-ear earphones, LAeq┬Ę8hŌĆÖs were 50.97-87.17 dBA (mean=56.58, standard deviation=7.58) and 39.77-88.37 dBA (mean=54.50, standard deviation=11.40) (Fig. 1). No one exceeded the criterion of KOSHA, but one listener exceeded the criterion of NIOSH.
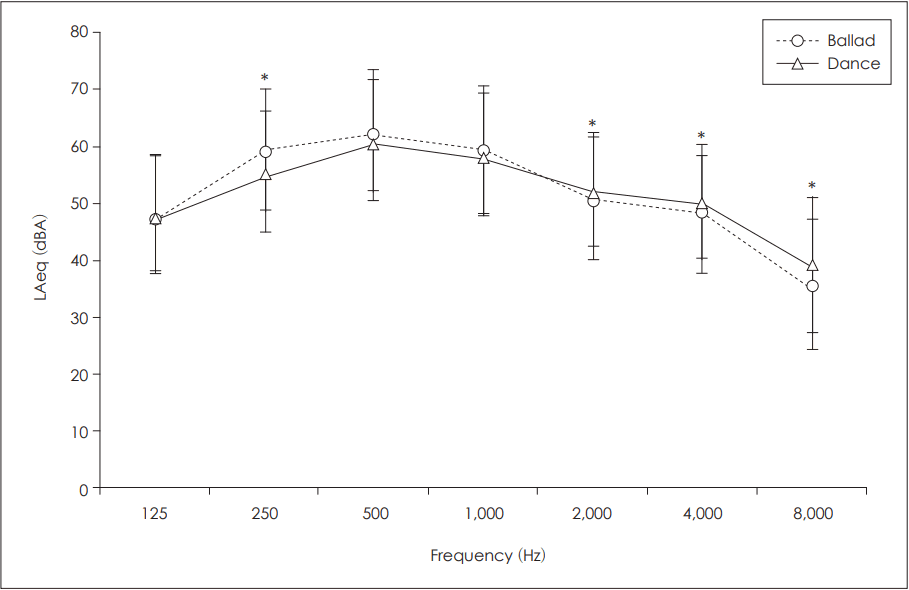
When the frequency characteristics of ballad and dance music genres were measured at PLLs, the greatest ouput levels were recorded at 0.5 kHz followed by 1, 0.25, 2, 4, 0.125, and 8 kHz. When paired sample t-test was performed for two music genres, significant differences at the four frequencies of 0.25, 2, 4, and 8 kHz were observed (p<0.05). At 0.25 kHz, the output level of dance music was lower than that of ballad. On the other hand, at frequencies of 2, 4, and 8 kHz, the output levels of dance music were significantly higher than those of ballad (Fig. 2).
As the volume increased by an interval of 25%, the LAeq of both earphone types increased the output levels by approximately 15 dBA. For both music genres, the PLLs and the maximum output levels were higher for earbuds than over-the-ear earphones showing agreement with the results of other studies [7,10,11]. The volume levels of the maximum settings of this study were 104.3-117.9 dBA which could be dangerous on userŌĆÖs hearing sensitivity. Considering the recommendation standard provided in 2013 by the Ministry of Environment Korea was lower than 100 dBA for smartphone MP3 players, the maximum volume setting could be harmful [23]. However, only one participant exceeded the criterion of NIOSH, when LAeq was converted to eight-hour equivalent continuous loudness level. Strangely, recent study observed the same result that only one participant out of 117 exceeded the daily noise dose [1]. At this previous study which did investigation by self-reporting of actual listening habits, the researchers suggested the feasibility of monitoring listening habits by a smartphone application. This may be a very good idea considering the fact that 95% of college students were unaware of the potential risk of the PLD [2]. 1 in 4 found to listen to their PLDs at dangerous level when the output levels were measured at free-field equivalent levels [2]. Although, our results showed safe listening range except one participant, we agree that there should be a good standard for the output levels of PLDs and be a good guide for listening habits of music for young adults. Because our results were obtained at the quiet environment, we could not provide the reality of the exposure to PLDs of them. At the real situation, they listen to the music with their PLDs in background noise and they probably expose to the high intensity environment such as live concerts, bars, and night clubs, frequently. About 50% of the participant out of 180 college students reported exposure to loud noise events at bars or concerts [2]. Counting the higher level of PLDs with background noise [8], the real sound levels for young adults hear could be hazardous.
However, the personal preference for listening loudness seemed to affect PLLs by music genre showing the difference in PLLs between electronica and hip-hop in one study [15]. Although, the music genre have produced mixed results about maximum output levels, the output levels of rock music seemed to produce the higher output levels among several music genres [4,9,12]. In the light of difference by music genres, the frequency characteristic of music genres showed the higher PLLs at 0.5, 1, 0.25, 2, 4, 0.125, and 8 kHz in the order of the present study. Also, the output levels of ballad and dance showed significant differences in 0.25, 2, 4, and 8 kHz. And up to 1 kHz the ballad showed higher levels. The reason was postulated as the characteristic of ballad music carrying story-centered features. The result of this frequency analysis was very similar to Hong and Park [24] which indicated about same PLLs up to 1 kHz when compared to dance and rock. In this study, about 1 kHz, the PLLs of dance and rock got higher than ballad.
We hypothesized that longer listening duration might affect PPL changes that are statistically significant. In this study, for 60 minutes duration, listeners hardly adjusted their PLLs compared to those of 30 minutes duration. The 60 minutes duration might be short to make differences. Since college students thought 30, 60, 120, and 180 minutes to be harmful for 11, 34, 36, 19% [2], we could presume that many college students listened to music longer than 60 minutes. Potentially harmful noise levels increased as the duration increased, the alarm of listening duration also should be provided to young adults. Also, we hypothesized the earphone types and music genres would show the differences on PLLs, but the results did not indicate any significant difference. But, earbud, ballade, and 30 minutes showed higher PLL levels for 1.61, 1.23, and 0.94 dBA than over-the-ear, dance, and 60 minutes variables. However, the results found that all the participants listened within the safe range based on the NIOSH criteria with LAeq┬Ę8h except one participant. Therefore, we could recommend to educate better listening habits for music to young adults. It was naturally concluded this way, considering there were other factors contributing PLLs for music genres and listening duration such as frequency characteristics of the music, and the background noise. The earphone type seemed to be safer with over-the-ear earphone. Also, the combination of the over-the-ear earphone with dance music showed the lowest levels, when the volume settings were selected for the PLLs. Based on the findings to this study, overthe-ear earphone which showed lower PLL seemed to be more suitable to prevent noise induced hearing loss. The reason was speculated as better isolation from the background noise by covering ears.
The limitations of the present study can be stated that the quiet environmental conditions might have not accurately reflected the reality with background noise. Also, in the future distortion product otoacoustic emission tests, which are known to be sensitive to noise-induced hearing loss, should be performed for the physiological information.
Fig.┬Ā1.
Distribution of estimated output levels of LAeq┬Ę8h with earbud and over-the-ear earphones. A: Ballad and 30 min. B: Dance and 30 min. C: Ballad and 60 min. D: Dance and 60 min. LAeq: loudness A-weight equivalent.
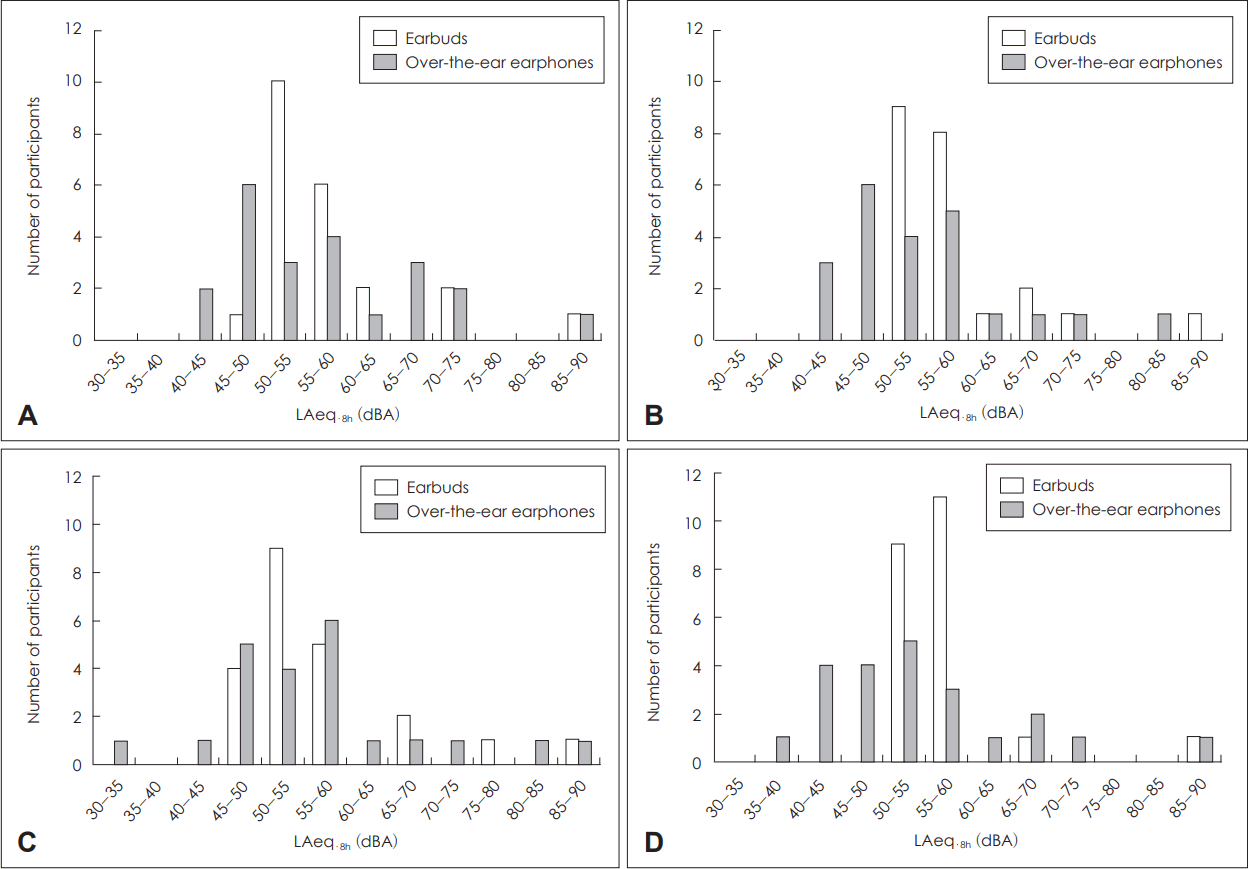
Fig.┬Ā2.
The frequency characteristics of ballade and dance music genres at prefered listening levels. LAeq: loudness A-weight equivalent. *p< 0.05.
Table┬Ā1.
LAeq and LAFmax depending on earphone types and music genres at four volume setting for 30 minutes
Table┬Ā2.
The volume setting numbers and output levels for preference listening levels according to music genres and earphone types
Table┬Ā3.
Average preferred listening levels in dBA according to 3 variables
REFERENCES
1. Kaplan-Neeman R, Muchnik C, Amir N. Listening to music with personal listening devices: monitoring the noise dose using a smartphone application. Int J Audiol 2017;56:400ŌĆō7.


2. Hutchinson Marron K, Marchiondo K, Stephenson S, Wagner S, Cramer I, Wharton T, et al. College studentsŌĆÖ personal listening device usage and knowledge. Int J Audiol 2015;54:384ŌĆō90.


3. Biassoni EC, Serra MR, Richtert U, Joekes S, Yacci MR, Carignani JA, et al. Recreational noise exposure and its effects on the hearing of adolescents. Part II: development of hearing disorders. Int J Audiol 2005;44:74ŌĆō85.


4. Kim J. Analysis of factors affecting output levels and frequencies of MP3 players. Korean J Audiol 2013;17:59ŌĆō64.



5. Kumar A, Mathew K, Alexander SA, Kiran C. Output sound pressure levels of personal music systems and their effect on hearing. Noise Health 2009;11:132ŌĆō40.


6. Dai W, Yu K. Contestability in the digital music player market. SSRN [serial online] 2015 Aug 19 [cited 2016 Feb 22]. Available from: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2736088.

7. Portnuff CD, Fligor BJ, Arehart KH. Teenage use of portable listening devices: a hazard to hearing? J Am Acad Audiol 2011;22:663ŌĆō77.


8. Kim WK, Jung JY, Suh MW. Effects of earphone style and noise environment on listening levels when using portable music players in the laboratory. Commun Sci & Dis 2011;16:408ŌĆō15.

9. Fligor BJ, Cox LC. Output levels of commercially available portable compact disc players and the potential risk to hearing. Ear Hear 2004;25:513ŌĆō27.


10. Henry P, Foots A. Comparison of user volume control settings for portable music players with three earphone configurations in quiet and noisy environments. J Am Acad Audiol 2012;23:182ŌĆō91.


11. Keppler H, Dhooge I, Maes L, DŌĆÖhaenens W, Bockstael A, Philips B, et al. Short-term auditory effects of listening to an MP3 player. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2010;136:538ŌĆō48.


12. Breinbauer HA, Anabal├│n JL, Gutierrez D, C├Īrcamo R, Olivares C, Caro J. Output capabilities of personal music players and assessment of preferred listening levels of test subjects: outlining recommendations for preventing music-induced hearing loss. Laryngoscope 2012;122:2549ŌĆō56.


13. Hodgetts WE, Rieger JM, Szarko RA. The effects of listening environment and earphone style on preferred listening levels of normal hearing adults using an MP3 player. Ear Hear 2007;28:290ŌĆō7.


14. Portnuff CDF, Fligor BJ. Sound output levels of the iPod and other MP3 players: is there potential risk to hearing? In: Proceedings of the NIHL in Children Conference; 2006 Oct 19; Cincinnati, OH.
15. Ahmed S, Fallah S, Garrido B, Gross A, King M, Morrish T, et al. Use of portable audio devices by university students. J Can Acoust Assoc 2007;35:35ŌĆō52.
16. International Organization for Standardization. ISO 1999. Acoustics: determination occupational noise exposure and estimation of noise induced hearing impairement. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization;1990.
17. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Occupational noise exposure: revised criteria 1998. Cincinnati, OH: Department of Health and Human Services;1998.
19. Worthington DA, Siegel JH, Wilber LA, Faber BM, Dunckley KT, Garstecki DC, et al. Comparing two methods to measure preferred listening levels of personal listening devices. J Acoust Soc Am 2009;125:3733ŌĆō41.



20. Levey S, Levey T, Fligor BJ. Noise exposure estimates of urban MP3 player users. J Speech Lang Hear Res 2011;54:263ŌĆō77.


21. American National Standards Institute. Maximum permissible ambient noise levels for audiometric test rooms (ANSI S3.1-1999). American National Standards Institute;1999.
22. Occupational Safety and Health Administration. OSHA Regulations (Standards-29 CFR): OC Occupational Noise Exposure.-1910. 95, Appendix D-Audiometric test rooms [cited 2017 Nov 28]. Available from: https://www.osha.gov/pls/oshaweb/owadisp.show_document?p_table= STANDARDS&p_id=9739.
23. Ministry of Environment. Maximum volume recommended standard of portable audio devices [cited 2012 Jul 16]. Available from: http://me.go.kr/home/web/board/read.do;jsessionid=BppI7NIA6Sn5anS0mtkbr3Y9caqsurf71o6NGDf1x3id9oE2O7Ivj56rAmaNgDjQ.meweb2vhost_servlet_engine1?pagerOffset=2120&maxPageItems=10&maxIndexPages=10&searchKey=&searchValue=&menuId=&orgCd=&boardMasterId=1&boardCategoryId=39&boardId=182092&decorator=.
24. Hong SW, Park MY. A study on possibility of hearing loss and the actual conditions of noise exposure in the use of portable cassette players. In: Proceeding of the conference on Korean Operations Research and Management Science Society and Korean Institute of Industrial Engineers; 1997 Apr 25-26; Pohang. Seoul. In: Korean Institute Of Industrial Engineers; 1997 531ŌĆō4.